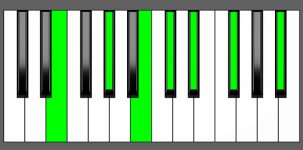
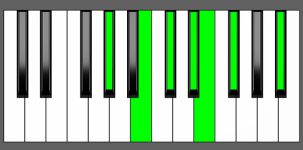
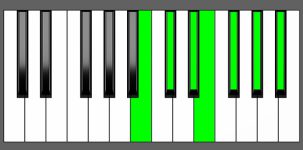
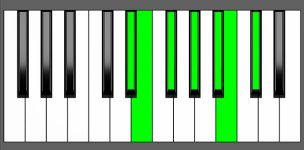
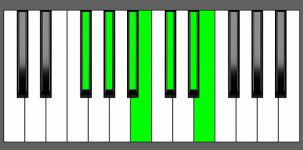
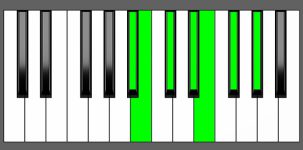
Piano Diagram of Dbm13 in Root Position

The Dbm13 chord is built upon the root note Db and includes a minor 3rd (Fb), a perfect 5th (Ab), a minor 7th (Cb), a major 9th (Eb), an 11th (Gb), and a 13th (Bb). This chord bears resemblance to a minor 6th chord due to the presence of the 13th, which is essentially a 6th note played at a higher octave. However, it also includes a minor 7th, major 9th, and 11th notes, which contribute to creating a sense of tension and dissonance.
Structure of Dbm13
Notes |
|---|
| Db, Fb, Ab, Cb, Eb, Gb, Bb |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, m3, 5, m7, 9, 11, 13 |
Playing Extended Chords on Piano
Extended chords like the Dbm13 can be challenging to play due to the large number of notes they involve. To simplify them, pianists often use different strategies like omitting certain notes or dividing the chord between both hands.
How to play a Dbm13
When playing a Dbm13 chord, you can play the root note Db with the left hand and use the right hand to play the minor 7th note Cb (B), the 9th note Eb, and the 13th note Bb. This way, you can play a simplified Dbm13 chord that includes only the root note, minor 7th, 9th, and 13th notes:
Db + Cb, Eb, Bb
Another option is to play the root note with the left hand and use the right hand to play an inversion of the chord with the 7th note Cb (B), the minor 3rd note Fb (E), and the 13th note Bb:
Db + Cb, Fb, Bb
Also, you could play a Dbm13 just playing the root note with the left hand and the 9th, the 3rd, and the 13th with your right hand:
Db + Eb, Fb, Bb
Despite using these techniques, extended chords can still produce dense and complex harmonies. When the chords are inverted, the resulting clusters of notes can be particularly challenging to play effectively and require careful voicing.
Dbm13 Chord Inversions
The Dbm13 chord has a total of 6 inversions:
| Root Position: | Db | Fb | Ab | Cb | Eb | Gb | Bb |
| 1st Inversion: | Fb | Ab | Cb | Db | Eb | Gb | Bb |
| 2nd Inversion: | Ab | Cb | Db | Eb | Fb | Gb | Bb |
| 3rd Inversion: | Cb | Db | Eb | Fb | Gb | Ab | Bb |
| 4th Inversion: | Eb | Fb | Gb | Ab | Bb | Cb | Db |
| 5th Inversion | Gb | Ab | Bb | Cb | Db | Eb | Fb |
| 6th Inversion | Bb | Cb | Db | Eb | Fb | Gb | Ab |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
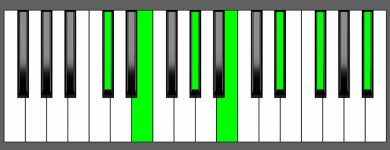
Chord Inversion on Piano
Having a solid understanding of chord inversions is a crucial element of music theory since it sheds light on how chords are constructed. When it comes to playing chord inversions on a piano, it’s essential to keep in mind that the charts and graphs depicting the order of notes may not always be feasible or even playable.
To achieve the proper chord voicings on a piano, you must spread the chord notes across various octaves and positions on the keyboard. This often entails deviating from the typical shape of the chord’s inversions shown in charts, which may not be the most practical or comfortable way to play the chord.
While chord inversion charts can be helpful in understanding the structure and sequence of notes in a chord, it’s always a good idea to experiment with different voicings and fingerings to find the most efficient and comfortable way to play the chord, while still preserving its intended harmonic function and sound.
Music Theory and Harmony of Dbm13
The Dbm13 chord is a diatonic extension of Dbm7. While it can be substituted for the Dbm7 chord in any position, it is commonly used in conjunction with it. Nonetheless, it’s worth noting that certain positions may not be as effective when substituting Dbm13 for Dbm7.
Building the Dbm13 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the Db Major Scale
To build a minor 13th chord, you would typically combine the root note, minor 3rd, 5th, minor 7th, major 9th, 11th, and 13th from a minor scale. However, for educational purposes, it may be clearer to demonstrate its construction using a major scale, as it better illustrates the relationship between intervals and their qualities.
To build a Dbm13, you can start with the Db Major scale:


To create a Dbm13 chord, apply the formula R, m3, 5, m7, 9, 11, 13 in the following way:
- Begin with the Root note, Db.
- Select the 3rd interval, F then subtract a half-step to get the minor 3rd E, which we call Fb to preserve the basic interval structure of the chord.
- Add the 5th interval, Ab.
- Select the 7th interval, C, and lower it down by a half-step to get the minor 7th, Cb (B).
- Add the major 9th, Eb.
- Pick the 11th Gb, which is a 4th interval at the higher octave.
- Lastly, add the 13th (Bb) which is a 6th at a higher octave.
By following this simple formula, you can create a minor 13th chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals
One method to create a minor 13th chord is by combining specific intervals – a minor 3rd, a major 3rd, a minor 3rd, a major 3rd, a minor 3rd, and a major 3rd. This is the formula:
m3 + 3 + m3 + 3 + m3 + 3 = minor 13th Chords
Upon analysis of the Dbm13 chord, we can note that:
- the interval between Db and Fb is a minor 3rd,
- between Fb and Ab is a major 3rd,
- between Ab and Cb is a minor 3rd,
- between Cb and Eb is a major 3rd,
- between Eb and Gb there is a minor 3rd,
- and finally, between Gb and Bb there is a major 3rd.
by Combining Chords
Another way to build minor 13th chords is by combining a minor triad with a Maj 7th chord derived from its minor 7th, or by merging a minor 7th chord with a minor triad that is based on its second interval.
To build a Dbm13 chord, you can blend a Db minor triad (Db, Fb, Ab) with a Cb Maj7 chord (Cb, Eb, Gb, Bb) or a Dbm7 (Db, Fb, Ab, Cb) with an Eb minor (Eb, Gb, Bb).
Dbm + Cb Maj7 = Dbm13
or
Dbm7 + Eb min = Dbm13
How to Use Dbm13 in a Chord Progression
The Db minor 13th chord is a more complex version of the Db minor 7th chord, as it includes additional notes such as the 9th, 11th, and 13th. These extra notes add a lot of dissonance and tension to the chord, which can make it tricky to use in a chord progression. Even if you leave out some of the notes, you still need to find the right voicing, because the effect of the Dbm13 depends on how it fits in with the other chords. It’s important to experiment with different voicings and figure out what works best with your particular progression.
In this post, we will focus just on the most common uses of the Dbm13 chord. The tables of the major and minor keys below include the Db minor 7th chord, which can be substituted or complemented by a Db minor 13th chord.
Dbm13 in Theoretical Keys
Except for the key of Ab minor, where the Db minor chord naturally occurs, all other keys are considered theoretical. In these cases, it is common practice to refer to their enharmonic equivalent keys for simplicity and practicality.
on Natural minor Scales
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Db = C# | C#m7 ⇒ C#m13 = Dbm13 | D#m7b5 | E Maj7 | F# min7 | G# min7 | A Maj7 | B7 |
| Ab | Ab min7 | Bbm7b5 | Cb Maj7 | Dbm7 ⇒ Dbm13 | Eb min7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
| Gb = F# | F# min7 | G#m7b5 | A Maj7 | B min7 | C#m7 ⇒ C#m13 = Dbm13 | D Maj7 | E7 |
- Tonic chord in C# minor as C#min13
- Subdominant chord in Ab minor
- Non-diatonic Dominant chord in F# minor as C#min13
on Major Scales
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cb = B | B Maj7 | C#m7 ⇒ C#m13 = Dbm13 | D# min7 | E Maj7 | F#7 | G# min7 | A#m7b5 |
| Bbb = A | A Maj7 | B min7 | C#m7 ⇒ C#m13 = Dbm13 | D Maj7 | E7 | F# min7 | G#m7b5 |
| Fb = E | E Maj7 | F# min7 | G# min7 | A Maj7 | B7 | C#m7 ⇒ C#m13 = Dbm13 | D#m7b5 |
- Supertonic chord in B Major as C#min13
- Non-diatonic Mediant chord in A Major as C#min13
- Submediant chord in E Major as C#min13
Dbm13 as Tonic Chord in Db minor
Check C#m13 as Tonic Chord in C# minor
Dbm13 as Subdominant Chord in Ab minor
The Db minor 13th can also be played as the subdominant chord in the key of Ab minor.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| Ab min7 | Bbm7b5 | Cb Maj7 | Db min7 | Eb min7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
Dbm13 Chord Progressions as iv degree
The following chord progressions feature a Dbm13 chord as the subdominant (iv degree):
iv III VI VII
| iv | III | VI | VII |
| Dbm13 | Dbm7 | Cb Maj7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
i iv VI v
| i | iv | VI | v |
| Ab min7 | Dbm13 | Dbm7 | Fb Maj7 | Eb min7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| Ab min7 | Dbm13 | Dbm7 | Gb7 | Cb Maj7 | Fb Maj7 | Bbm7b5 | Eb7 | Ab min7 |
Dbm13 as Dominant Chord in Gb minor (Non-Diatonic)
Check C#m13 as Dominant Chord in F# minor
Dbm13 as Supertonic Chord in Cb Major
Check C#m13 as Supertonic Chord in B Major
Dbm13 as Mediant Chord in Bbb Major (Non-Diatonic)
Check C#m13 as Mediant Chord in A Major
Dbm13 as Submediant Chord in Fb Major
Check C#m13 as Submediant Chord in E Major
Alternative Dbm13 Nomenclature
- Db m13
- Db m13th
- Db m11/13
- Db min13th
- Db minor 13
- Db m7/9/11/13
- Db minor thirteenth