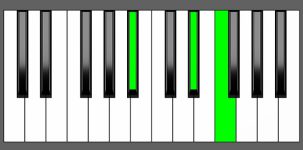
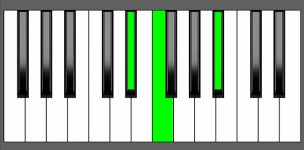
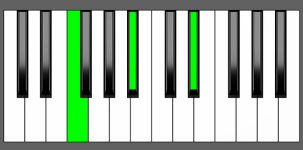
Piano Diagram of Bbsus4 in Root Position

The Bb suspended fourth (Bbsus4) chord consists of three notes: Bb, Eb, and F. It’s called a “suspended 4” chord because the third note of the chord is replaced with a perfect fourth. To play the Bbsus4 chord on a piano, you would start with a Bb major chord and replace the third note D, with the fourth note Eb. Further reading will give you a better understanding of the music theory principles behind this chord.
Structure of Bbsus4
Notes |
|---|
| Bb, Eb, F |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, 4, 5 |
Fingers Position
Left Hand |
|---|
| 4, 2, 1
5, 2, 1 |
Right Hand |
|---|
| 1, 3, 4
1, 4, 5 |
Bbsus4 Chord Inversions
The Bbsus4 chord has a total of 2 inversions:
| Root Position: | Bb | Eb | F |
| 1st Inversion: | Eb | F | Bb |
| 2nd Inversion: | F | Bb | Eb |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Bbsus4 Chord Equivalencies
An interesting detail about sus4 chords is that their 1st inversion results in a sus2 chord. To clarify, when the 4th note of a sus4 chord becomes the root note, it transforms into a sus2 chord.
1st Inversion of Bbsus4 = Ebsus2
For instance, if we take the Bbsus4 chord with the notes Bb, Eb, and F and rearrange them so that Eb becomes the root note, we end up with an Ebsus2 chord with the notes Eb, F, and Bb. Therefore, the 1st inversion of Bbsus4 is equivalent to Ebsus2.
Music Theory and Harmony of Bbsus4
What are Suspended Chords?
Suspended chords are a type of chord in which the third note is replaced by either a major second or a perfect fourth. These resulting chords are called suspended second (sus2) or suspended fourth (sus4) chords, respectively. These chords create a unique and sometimes unresolved sound that can add tension and interest to a musical composition.
Suspended chords have a distinct sound that sets them apart from major and minor chords. They are called suspended chords because they temporarily suspend the listener’s expectation of hearing a major or minor stable chord. Instead, they feature a perfect fourth or major second interval in place of the third. Due to their “neutral nature,” suspended chords can sometimes be used as substitutes for both major and minor chords.
Building the Bbsus4 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the Bb major Scale
To build a sus4 chord, you can use the major scale as a guide and combine a root note, a perfect 4th interval, and a perfect 5th interval.


To create a Bbsus4 chord, apply the formula R, 4, 5 in the following manner:
- Begin with the Root note, which is Bb.
- Select the 4th interval, which is Eb, and add it to the chord.
- Finally, add the 5th interval, which is F.
By following this simple formula, you can create a sus4 chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals
One method to create a suspended 4th chord is by combining two specific intervals – a perfect 4th, and a major 2nd.
4 + 2 = sus4 Chords
To illustrate, let’s use the Bbsus4 chord as an example. By examining the intervals between the notes, we can see that Bb-Eb forms a perfect 4th interval, and Eb-F creates a major second interval (a whole tone).
How to Use Bbsus4 in a Chord Progression
Suspended chords have a unique quality that sets them apart from major and minor chords. They are considered neither major nor minor, which makes them a great tool for creating tension and suspense in a musical composition before resolving to a stable major or minor chord.
In the following tables, you will find the harmonization of the major and relative natural minor scales for keys that include Bb major and Bb minor chords in various positions and different harmonic roles.
Bbsus4 as Substitute of Bb Maj Chords
In the key of F Major and D minor, the 4th note Eb can clash with the D and the E note that is present in those keys. While this doesn’t prevent you from using the Bbsus4 chord in those positions, it’s important to be aware that it can create a strong dissonance with the melody or other elements of the composition.
on Major Scales
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bb | Bb Maj7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 | F Maj7 | G min7 | Am7b5 |
| F | F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C Maj7 | D min7 | Em7b5 |
| Eb | Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C min7 | Dm7b5 |
- Tonic chord in Bb Major
- Non Diatonic Subdominant chord in F Major
- Dominant chord in Eb Major
on Natural minor Scales
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | G min7 | Am7b5 | Bb Maj7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
| D | D min7 | Em7b5 | F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C7 |
| C | C min7 | Dm7b5 | Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 ⇒ Bbsus4 |
- Mediant chord in G minor
- Non Diatonic Submediant chord in D minor
- Leading tone chord in C minor
Bbsus4 as Substitute of Bb min Chords
While the Bbsus4 chord can be used as a substitute or variation for Bb minor 7th chords, it’s important to note that a B7sus4 chord would be a better fit due to the presence of the minor 7th.
on Major Scales
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ab | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C min7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 | F min7 | Gm7b5 |
| Gb | Gb Maj7 | Ab min7 | Bb min7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 | Eb min7 | Fm7b5 |
| Db | Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 | Bb min7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | Cm7b5 |
- Supertonic chord in Ab Major
- Mediant chord in Gb Major
- Submediant chord in Db Major
on Natural minor Scales
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bb | Bb min7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | Cm7b5 | Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 |
| F | F min7 | Gm7b5 | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | C min7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 |
| Eb | Eb min7 | Fm7b5 | Gb Maj7 | Ab min7 | Bb min7 ⇒ Bbsus4 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
- Tonic chord in Bb minor
- Subdominant chord in F minor
- Dominant chord in Eb minor
Bbsus4 Function in Major and Minor Keys
Understanding Scale Degrees
Scale degrees are essential for understanding the relationship between the notes in a scale and how they function within chords. The diatonic major scale consists of seven degrees, each with its unique role in creating the overall harmony of the scale.
- The first degree of the scale is known as the Tonic, which serves as the anchor for the music. It establishes a stable tonal center that acts as the foundation for the scale.
- The second degree is called the Supertonic, often used as a transitional note between the Tonic and other notes in the scale. It creates a sense of motion within the melody or harmony.
- The third degree of the scale is the Mediant, which sits halfway between the Tonic and Dominant notes. It helps establish whether the scale is major or minor.
- The fourth degree is called the Subdominant, used to complement the Dominant and add tension and resolution to the music.
- The fifth degree is the Dominant, which creates tension and anticipation within the melody or harmony, typically resolved by returning to the Tonic.
- The sixth degree is the Submediant, often employed as a transitional note between the Dominant and Tonic, adding a sense of stability and restfulness to the music.
- The seventh degree is the Leading tone, located one half-step below the Tonic. It creates a strong sense of tension and a desire to resolve to the Tonic, frequently used to create a sense of resolution and finality in the melody or harmony.
Bbsus4 in Bb Major
The Bbsus4 chord can be used along with the Bb Maj7 chord (or any other kind of Bb major chord) to add color on the first degree. The Bbsus4 chord can suspend the Bb Major chord or the subsequent chord.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 | F7 | G min7 | Am7b5 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as I degree
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| C min7 | F7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 |
I IV V
| I | IV | V |
| Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
I V vi IV
| I | V | vi | IV |
| Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | F7 | G min7 | Eb Maj7 |
I IV vi V
| I | IV | vi | V |
| Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | Eb Maj7 | G min7 | F7 |
Bbsus4 in F Major (Non Diatonic)
Let’s explore the sound of the Bbsus4 chord in the key of F major, which can be used as a substitute or variation of the Bb Maj7 chord on the IV degree. However, it’s important to note that the Bbsus4 contains an Eb which clashes with the D and the E present in this key. The Bbsus4 chord is not diatonic in this key, so it may sound unusual or foreign to the overall tonality.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| F Maj7 | Gm7b5 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 | D min7 | Em7b5 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as IV degree
I IV V
| I | IV | V |
| F Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
I V vi IV
| I | V | vi | IV |
| F Maj7 | C7 | D min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 |
I IV vi V
| I | IV | vi | V |
| F Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | D min7 | C7 |
Bbsus4 in Eb Major
In the key of Eb Major, the fifth degree it features a Bb7 chord. Adding a Bbsus4 chord can create tension and expectation, leading to a resolution on the dominant chord. Note that using a B7sus4 chord instead of a Bbsus4 would be a better option in this case.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 | C min7 | Dm7b5 |
Bbsus4 as V degree – Chord Progressions
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 | Eb Maj7 |
I IV V
| I | IV | V |
| Eb Maj7 | Ab Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 |
I V vi IV
| I | V | vi | IV |
| Eb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 | C min7 | Ab Maj7 |
I IV vi V
| I | IV | vi | V |
| Eb Maj7 | Ab Maj7 | C min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 |
I IV ii V iii vi ii V
| I | IV | ii | V | iii | vi | ii | V |
| Eb Maj7 | Ab Maj7 | F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 | G min7 | C min7 | F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 |
Bbsus4 in G Minor
Try experimenting with chord progressions featuring a BMaj7 on the III degree of the G minor scale, and try playing a Bbsus4 before or after the BMaj7 to see how it sounds.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| G min7 | Am7b5 | Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as III degree
i III
| i | III |
| G min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 |
i III VII VI
| i | III | VII | VI |
| G min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | F7 | Eb Maj7 |
i III iv v
| i | III | iv | v |
| G min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 |
i III ii v
| i | III | ii | v |
| G min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | Am7b5 | D min7 |
I iii vi V
| i | III | VI | iv |
| G min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | Eb Maj7 | C min7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| G min7 | C min7 | F7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | Eb Maj7 | Am7b5 | D7 | G min7 |
Bbsus4 in D Minor (Non Diatonic)
In the key of D minor, the VI degree chord is a Bb major chord. To add some color, you can use a Bbsus4 chord as a substitution or variation of this chord. However, keep in mind that the Bbsus4 chord is non-diatonic in this key because it contains an Eb while the D minor scale contains a D and an E. Therefore, it’s generally recommended to avoid using the Bbsus4 chord in this key but feel free to experiment and see how it sounds to your ears.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| D min7 | Em7b5 | F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as VI degree
i VI VII
| i | VI | VII |
| D min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
i v VI VII
| i | v | VI | VII |
| D min7 | A min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
i III VII VI
| i | III | VII | VI |
| D min7 | F Maj7 | C7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| D min7 | G min7 | C7 | F Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb Maj7 | Em7b5 | A7 | D min7 |
Bbsus4 in C Minor
Let’s explore the use of Bbsus4 as a leading tone chord in the key of C minor. As the leading tone chord, Bbsus4 can create tension and lead the listener’s ear to the tonic chord, which is C minor in this case.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| C min7 | Dm7b5 | Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 |
Bbsus4 as VII degree – Chord Progressions
i VI VII
| i | V | VII |
| C min7 | G min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 |
i v VI VII
| i | v | VI | VII |
| C min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 | Bbsus4 |
i III VII VI
| i | III | VII | VI |
| C min7 | Eb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 | Ab Maj7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| C min7 | F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb7 | Eb Maj7 | Ab Maj7 | Dm7b5 | G7 | C min7 |
Bbsus4 in Ab Major
In the key of Ab Major, the supertonic chord is a Bb minor. However, we can use a Bbsus4 chord as a variation or substitution for the Bbm chord to add some tonal color and interest to a chord progression.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 | F min7 | Gm7b5 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as ii degree
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Eb7 | Ab Maj7 |
I IV ii V iii vi ii V
| I | IV | ii | V | iii | vi | ii | V |
| Ab Maj7 | Db Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Eb7 | C min7 | F min7 | Bmin7 | Bbsus4 | Eb7 |
Bbsus4 in Gb Major
In the key of Gb Major, the Bbsus4 chord can be used on the III degree.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Gb Maj7 | Ab min7 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 | Eb min7 | Fm7b5 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as iii degree
I iii IV V
| I | iii | IV | V |
| Gb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
I iii ii V
| I | iii | ii | V |
| Gb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Ab min7 | Db7 |
I iii vi IV
| I | iii | vi | IV |
| Gb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Eb min7 | Cb Maj7 |
Bbsus4 in Db Major
Let’s explore how the Bbsus4 chord can function as a submediant chord in the key of Db major. You can try incorporating it into chord progressions that feature a Bbm chord on the VI degree.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 | Bb min7 | Cm7b5 |
Bbsus4 as vi degree – Chord Progressions
I iii vi V
| I | iii | vi | V |
| Db Maj7 | F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Ab7 |
I vi ii V
| I | vi | ii | V |
| Db Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Eb min7 | Ab7 |
I IV ii V iii vi ii V
| I | IV | ii | V | iii | vi | ii | V |
| Db Maj7 | Gb Maj7 | Eb min7 | Ab7 | F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Eb min7 | Ab7 |
Bbsus4 in Bb Minor
When using the Bbsus4 chord in the key of Bb minor, it can be a great variation for the traditional Bbm chord. It creates a more ambiguous sound due to its suspended nature, but it can be used to add tension or to create a unique texture in a chord progression.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| Bb min7 | Cm7b5 | Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as i degree
i VI VII
| i | VI | VII |
| Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 |
Modulation
| isus4 | i | isus2 | i |
| Bbsus4
Bb (F, Bb, Eb) |
Bb min
Bb (F, Bb, Db) |
Bbsus2
Bb (F, Bb, C) |
Bb min
Bb (F, Bb, Db) |
Use your left hand to play the Bb root note, and your right hand to play the remaining notes of the chord.
i iv VI VII
| i | iv | VI | VII |
| Bbsus4 | Eb min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 |
Bbsus4 in F Minor
In F minor, the IV degree is Bb major, which can be replaced or varied with a Bbsus4 chord.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| F min7 | Gm7b5 | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 |
Bbsus4 Chord Progressions as iv degree
iv III VI VII
| iv | III | VI | VII |
| Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Ab Maj7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 |
i iv VI v
| i | iv | VI | v |
| F min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Db Maj7 | C min7 |
Bbsus4 in Eb Minor
In the key of Eb minor, the Bbsus4 chord can be used on the v (fifth) degree.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| Eb min7 | Fm7b5 | Gb Maj7 | Ab min7 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
Bbsus4 as v degree – Chord Progressions
i iv VI v
| i | iv | VI | v |
| Eb min7 | Ab min7 | Cb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 |
i v VI VII
| i | v | VI | VII |
| Eb min7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
i VI v iv
| i | VI | v | iv |
| Eb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Bbsus4 | Bb min7 | Ab min7 |
Alternative Names for Bbsus4
- Bbsus4
- Bbsus(4)
- Bb add4(no3)
- Bb add4(omit3)
- Bb Suspended 4th
Conclusion
While the chord progressions and examples in this post offer a comprehensive overview of common uses for the Bbsus4 chord, space constraints prevent a full exploration of advanced harmony topics. These include chord progressions based on scales, modal interchange, and jazz harmony. However, I encourage readers to continue studying and exploring to gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic possibilities beyond the basic concepts presented here. You can unlock a wide range of musical expressions and expand your creativity.
I hope this post has been informative and helpful in your music theory journey. Keep exploring and creating music, and don’t forget to have some fun along the way!