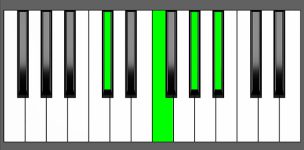
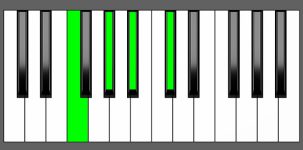
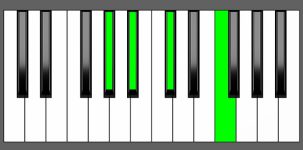
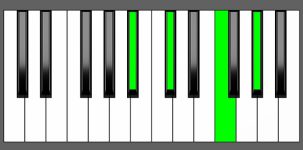
Piano Diagram of C#6 in Root Position

C#6 is a four-note chord consisting of the notes C#, E#, G#, and A#. It is a major chord with an added sixth. It belongs to the chord family of “added tone chords” (aka “add chord”). Keep reading to gain a deeper understanding of the music theory behind this chord.
Structure of C#6
Notes |
|---|
| C#, E#, G#, A# |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, 3, 5, 6 |
Finger Position
Left Hand |
|---|
| 5, 3, 2, 1
5, 4, 2, 1 |
Right Hand |
|---|
| 1, 2, 4, 5
1, 2, 3, 4 |
C#6 Chord Inversions
The C#6 chord has a total of 3 inversions:
| Root Position: | C# | E# | G# | A# |
| 1st Inversion: | E# | G# | A# | C# |
| 2nd Inversion: | G# | A# | C# | E# |
| 3rd Inversion: | A# | C# | E# | G# |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Music Theory and Harmony of C#6
Building the C#6 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the C# Major Scale
To create a 6th chord, you can use the Major scale as a reference by combining a Root, a 3rd, a 5th, and a 6th.


Apply the formula R, 3, 5, 6 to build a 6th chord:
- Select the Root note, which is C#.
- Pick the 3rd note, which is E# (F), and add it to the chord.
- Add the 5th note, which is G#, and include it as well.
- Finally, add the 6th which is A#.
by Combining Intervals
To build a 6th chord, one approach is to combine specific intervals, namely a major 3rd, a minor 3rd, and a major 2nd (a whole-tone).
3 + m3 + 2 = 6th chords
For instance, when building a C#6 chord, you can observe that
- C#-E# forms a major 3rd interval,
- E#-G# creates a minor 3rd interval, and
- G#-A# makes up a whole-tone interval.
By stacking these intervals together, you can form a C#6 chord.
6th Chords Equivalencies
If we take the third inversion of a 6th chord (which means we move the notes around so that the 6th note becomes the Root note), we end up with a new chord that is equivalent to a min7 chord.
So, if we take the C#6 chord (which has the notes C#, E#, G#, and A#) and move the notes around so that A# becomes the Root note, we end up with a new chord that is equivalent to an A# min7 chord (which has the notes A#, C#, E#, and G#).
3rd inversion of C#6 = A# min7
How to Use C#6 in a Chord Progression
Since 6th are based on major triads with an extra sixth, they can substitute the major chords built on the scale of the root. This means that we can use the C#6 chord in those positions on the scale where the harmonization results in a major chord.
This table showcases the harmonized major and natural minor scales where a C# Major chord can be found. In all positions where a C# Maj7 chord is present, the C#6 chord can be used as a variation.
on Major Scales
Since G# Major is a theoretical key, we will refer to its enharmonic equivalent key Ab Major.
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C# | C# Maj7 ⇒ C#6 | D# min7 | E# min7 | F# Maj7 | G#7 | A# min7 | B#m7b5 |
| G# = Ab | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 ⇒ Db6 = C#6 | Eb7 | F min7 | Gm7b5 |
- Tonic chord in C# Major
- Subdominant chord in Ab Major as Db6
on Natural minor Scales
Instead of E# minor it’s more practical to refer to the more common F minor key.
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A# | A# min7 | B#m7b5 | C# Maj7 ⇒ C#6 | D# min7 | E# min7 | F# Maj7 | G#7 |
| E# = F | F min7 | Gm7b5 | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 ⇒ Db6 = C#6 | D#7 |
- Mediant chord in A# minor
- Submediant chord in F minor as Db6
C#6 in C# Major
The 6th interval is a consonant interval, which means it doesn’t create any tension that needs to be resolved. It’s stable and often used as a substitute for the tonic chord, which is usually the main chord in a musical piece.
The A6th chord can be used instead of a C# major (or C# major 7th chord), which is the first chord in the harmonized C# major scale.
In a major key, the I chord (built on the first degree of the major scale) serves as the tonic chord, providing the harmonic center of the chord progression.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| C# Maj7 ⇒ C#6 | D# min7 | E# min7 | F# Maj7 | G#7 | A# min7 | B#m7b5 |
C#6 Chord Progressions as I degree
Replacing a standard major chord with a 6th chord can enhance the richness and complexity of your music. Here’s a chord progression that demonstrates how the C#6 chord can function as a substitute for the tonic (I degree) in a chord progression:
II V I
| ii | V | I |
| D# min7 | G#7 | C#6 |
I IV V
| I | IV | V |
| C#6 | F# Maj7 | G#7 |
I V vi IV
| I | V | vi | IV |
| C#6 | G#7 | A# min7 | F# Maj7 |
I IV vi V
| I | IV | vi | V |
| C#6 | F# Maj7 | A# min7 | G#7 |
C#6 in G# Major
C#6 in A# minor
Similarly, in A# minor, the C#6 chord can be used as a substitute for the C# Maj7 chord on the third degree.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| A# min7 | B#m7b5 | C# Maj7 ⇒ C#6 | D# min7 | E# min7 | F# Maj7 | G#7 |
C#6 as III degree – Chord Progressions
These chord progressions show the C#6 chord as a substitute for the mediant (III degree) chord.
i III
| i | III |
| A# min7 | C#6 |
i III VII VI
| i | III | VII | VI |
| A# min7 | C#6 | G#7 | F# Maj7 |
Circle Progression
| i | vi | VII | III | VI | ii | V | i |
| A# min7 | D# min7 | G#7 | C#6 | F# Maj7 | B# dim7 | E#7 | A# min7 |
C#6 in E# minor
Alternative Names for C#6 Chord
- Do#6
- C# 6th
- C# M6
- C# sixth
- C# add6
- C# Maj6
- C# major6
- C# major 6th
- C# major sixth
- C# major add 6th