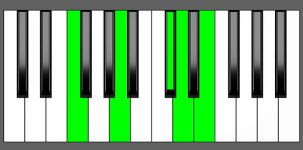
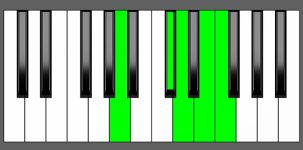
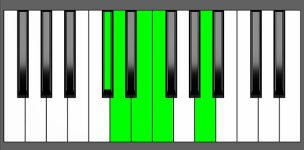
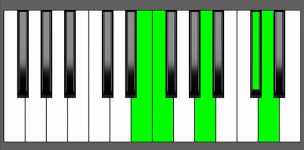
Piano Diagram of DmMaj9 in Root Position

The DmMaj9 chord, consisting of the notes D, F, A, C#, and E, is a minor chord that is built on the key of D and features an additional major 7th (C#) and a major 9th (E). Like the DmMaj7, it contains an augmented fifth so it’s pretty dissonant. In this article, we’ll explore the music theory underlying the DmMaj9 chord, including its construction, common voicings, and its role in chord progressions.
Structure of DmMaj9
Notes |
|---|
| D, F, A, C#, E |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, m3, 5, 7, 9 |
DmMaj9 Chord Inversions
The DmMaj9 chord has a total of 4 inversions:
| Root Position: | D | F | A | C# | E |
| 1st Inversion: | F | A | C# | D | E |
| 2nd Inversion: | A | C# | D | E | F |
| 3rd Inversion: | C# | D | E | F | A |
| 4th Inversion: | E | F | A | C# | D |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
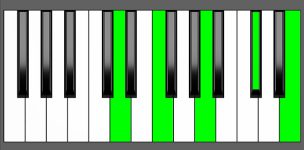
Chord Inversions on Piano
Chord inversion diagrams provide a visual representation of a chord’s structure and the different positions it can take on the keyboard. However, it’s important to note that not all of these positions are practical or comfortable to play. To effectively play chords on the piano, it’s essential to study voicing – the specific arrangement of notes in a chord, including their octave placement and distribution across the keyboard.
By experimenting with different voicings and fingerings, pianists can find the most comfortable and efficient way to play each chord while still preserving its intended sound and harmonic function. This can involve playing some notes of the chord in higher or lower octaves or breaking up the chord into smaller intervals to create a smoother and more balanced sound.
Music Theory and Harmony of DmMaj9
Building the DmMaj9 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the D Major Scale
A minor major 9th chord is built by combining the Root, a minor 3rd, a 5th, a major 7th, and a major 9th interval from a minor scale, however, for educational purposes, it may be clearer to demonstrate its construction using a major scale, as it better illustrates the relationship between intervals and their qualities.
For example, to build a DmMaj9 chord, you can start with the D Major scale:


To create a DmMaj9 chord, apply the formula R, m3, 5, 7, 9 in the following manner:
- Begin with the Root note, which is D.
- Add the minor 3rd interval, F.
- Include the 5th note, which is A.
- Add the major 7th C#.
- Finally, add the major 9th interval E, which is the 9th note of the scale.
By following this simple formula, you can create a minor major 9th chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals
Another way to build a minor major 9th chord is by combining specific intervals – a minor 3rd, a major 3rd, another major 3rd and a minor 3rd.
m3 + 3 + 3 + m3 = minor major 9th chords
If we observe the intervals between the notes, we can notice that:
- D-F creates a minor 3rd,
- F-A forms a major 3rd interval,
- A-C# is a major 3rd
- and C#-E is a minor 3rd interval.
By stacking these four intervals together, we can build the DmMaj9 chord.
by Combining Chords
Another trick to build a minMaj9 chord is by combining a minor triad with the major chord built on its fifth note. To create a DmMaj9 chord, for instance, you can combine a D minor triad (D, F, A) with an A Major chord (A, C#, E). These two chords share the note A, and when played together, they form a DmMaj9 chord.
D minor + A Major = DmMaj9
How to Use DmMaj9 in a Chord Progression
The DmMaj9 chord is a fuller and more dissonant version of the DmMaj7. It is characterized by the presence of a major 7th interval, which is not found in either the natural minor or major scales. It’s diatonic in other scales like the harmonic and melodic minor scale, which features a minor major seventh chord on their first degree.
Most common uses of DmMaj9
Typically, both the DmMaj7 and the DmMaj9 chords are used as passing chords, temporarily transitioning towards a more stable Dm7. Additionally, they can serve as ending chords in specific musical contexts. This is because both chords produce a mysterious and intriguing atmosphere, making them suitable for certain musical styles and compositions.
Non-diatonic positions in Natural minor and Major Scales
The major seventh interval of the DmMaj9 chord, which is C#, clashes with the C note present in both natural minor and major scales.
- The DmMaj9 chord is commonly used in the first degree of minor scales or on the sixth degree of major scales, as part of a chromatic progression towards a minor 7th chord.
- It can also be used on the fourth degree of minor scales and on the second degree of major scales.
- While less common, it can still be used on the fifth degree of both minor and major scales.
- The DmMaj9 chord is not commonly used as a standalone chord (except in endings).
Here are the tables of the major and natural minor scales that include the D minor 7th, which can be complemented by a DmMaj9 chord.
on Natural minor Scales
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | D min7 ⇒ DmMaj9 |
Em7b5 | F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
| A | A min7 | Bm7b5 | C Maj7 | D min7 ⇒ DmMaj9 | E min7 | F Maj7 | G7 |
| G | G min7 | Am7b5 | Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 ⇒ DmMaj9 | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
Non diatonic passing chord to the:
- Tonic chord in D Minor
- Subdominant chord in A Minor
- Dominant chord in G minor (less common)
on Major Scales
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | C Maj7 | D min7 ⇒ DmMaj9 | E min7 | F Maj7 | G7 | A min7 | Bm7b5 |
| Bb | Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 ⇒ DmMaj9 | Eb Maj7 | F7 | G min7 | Am7b5 |
| F | F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 | D min7 ⇒ DmMaj9 | Em7b5 |
Non diatonic passing chord to the:
- Supertonic chord in C Major
- Mediant chord in Bb Major (less common)
- Submediant chord in F Major
DmMaj9 Function in Major and minor Keys
The DmMaj9 chord does not belong to the diatonic set of chords and therefore does not have a specific functional role in major and minor keys’ harmonic progressions. However, it can be utilized to add tonal color in specific situations where modulation to a Dm7 chord is appropriate or feasible. Typically, this chord is found close to a variation of a D minor chord, such as Dm6, Dm7, or Dm9, to create diatonic or chromatic modulations.
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord in D minor
In the key of D minor, the DmMaj9 serves as a passing chord to the Tonic chord, Dm7. The chord’s major 7th note C#, clashes with the C note found in the D minor scale, creating a tension that needs to be resolved. This can be achieved by transitioning the chord to a more stable Dm7 chord, which typically occurs within the same measure as the DmMaj9 chord.
Alternatively, the DmMaj9 chord can be left alone as an ending chord, but it’s too dissonant to be played for a whole measure within a chord progression.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| D min7 | Em7b5 | F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord on the i degree
The following chord progressions are examples of how the D minor major 9th chord can serve as a passing chord toward the tonic chord (Dm7).
Chromatic modulation
| i | iΔ | i7 | i6 |
| D min | DmMaj9 | Dm7 | D min6 |
i VI VII III
| i | VI | VII | III |
| Dm9 | Dm7 | DmMaj9 | Dm7
D (F, A, C, E) | D (F, A, C, D) | D (E, F, A, C#) | D (F, A, C, D) |
Bb Maj7 | C7 | F Maj7 |
This modulation is just a suggestion, and the voicing provided is merely a recommendation. Play the root note D with your left hand and play the rest of the notes with your right hand.
i iv VI VII
| i | iv | VI | VII |
| Dm9 | Dm7 | DmMaj9 | Dm7 | G min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| Dm9 | Dm7 | DmMaj9 | Dm7 | Gm7 | C7 | F Maj7 | Bb Maj7 | Em7b5 | A7 | D min7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord in A minor
The DmMaj9 chord can be used as a passing chord in the A minor scale which has a D min7 on the fourth degree.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| A min7 | Bm7b5 | C Maj7 | D min7 | E min7 | F Maj7 | G7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord on the iv degree
The following chord progressions feature a DmMaj9 chord in modulation to the iv degree in the key of A minor
iv III VI VII
| iv | III | VI | VII |
| Dm9 | Dm6 | DmMaj9 | Dm6
D (F, A, C, E) | D (F, A, B, D) | D (E, F, A, C#) | D (F, A, B, D) |
C Maj7 | F Maj7 | G7 |
i iv VI v
| i | iv | VI | v |
| A min7 | Dm9 | Dm6 | DmMaj9 | Dm6 | F Maj7 | E min7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| A min7 | Dm7 | Dm(Maj9) | G7 | C Maj7 | F Maj7 | Bm7b5 | E7 | A min7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord in G minor
In the G natural minor scale, the DmMaj9 chord can serve as a passing chord within the fifth degree, Dm7.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| G min7 | Am7b5 | Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord on the v degree
i iv VI v
| i | iv | VI | v |
| G min7 | C min7 | Eb Maj7 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm9 | Dm |
i v VI VII
| i | v | VI | VII |
| G min7 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm7 | Dm6 | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
i VI v iv
| i | VI | v | iv |
| G min7 | Eb Maj7 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm7 | Dm6 | C min7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord in C Major
In the C major scale, the DmMaj9 chord can also serve as a passing chord on the ii degree.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| C Maj7 | D min7 | E min7 | F Maj7 | G7 | A min7 | Bm7b5 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord on the ii degree
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| Dm7 | DmMaj9 | G7 | C Maj7 |
Circle Progression
| I | IV | vii | iii | vi | ii | V | I |
| C Maj7 | F Maj7 | Bm7b5 | E min7 | A min7 | Dm7 | Dm(Maj9) | G7 | C Maj7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord in Bb Major
Another position where it could be possible to add some color modulating a Dm7 is in the Bb major scale on the iii degree.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Bb Maj7 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 | F7 | G min7 | Am7b5 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord on the iii degree
I iii IV V
| I | iii | IV | V |
| Bb Maj7 | Dm9 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm | Eb Maj7 | F7 |
I iii ii V
| I | iii | ii | V |
| Bb Maj7 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm9 | Dm | C min7 | F7 |
I iii vi IV
| I | iii | vi | IV |
| Bb Maj7 | Dm9 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm | G min7 | Eb Maj7 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord in F Major
You can play the DmMaj9 in a modulation on the sixth degree of the F major scale.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| F Maj7 | G min7 | A min7 | Bb Maj7 | C7 | D min7 | Em7b5 |
DmMaj9 as Passing Chord on the vi degree
I iii vi V
| I | iii | vi | V |
| F Maj7 | A min7 | Dm9 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm | C7 |
I vi ii V
| I | vi | ii | V |
| F Maj7 | Dm9 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm | G min7 | C7 |
Circle Progression
| I | IV | vii | iii | vi | ii | V | I |
| F Maj7 | Bb Maj7 | Em7b5 | A min7 | Dm9 | Dm | DmMaj9 | Dm | Gm7 | C7 | F Maj7 |
Alternative Names for DmMaj9 Chord
- D-Δ9
- D mM9
- D m(Δ9)
- D-Δmaj9
- D minΔ9
- D-(Maj9)
- D mM7/9
- D m7+(9)
- D-Δ(add9)
- D minorΔ9
- D mΔ add2
- D mΔ add9
- D min maj9
- D min/maj9
- D min(Maj9)
- D min(Maj9)
- D m(maj7/9)
- D m(+7) add2
- D m(+7) add9
- D minor(Maj9)
- D m(maj7) add9
- D m(maj7) add2
- D minor major 9
- D minor major 9th
Conclusion
The chord progressions and examples presented in this post provide a comprehensive overview of the most common uses of the DmMaj9 chord. It’s important to note, however, that many advanced harmony-related topics could not be included due to space constraints. These topics include chord progressions built on harmonic and melodic scales, modal scales, hidden tonality, secondary dominants and other chord substitutions, non-functional harmony and atonal music, modal interchange and borrowed chords, voice leading and counterpoint, chromatisms, jazz harmony…I mean, music theory is a huge topic!
Although I couldn’t cover all of these topics in my post, I encourage readers to continue exploring these areas in their own study and research. By expanding your knowledge in these advanced areas of music theory, you can gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic possibilities that exist beyond the basics presented here.