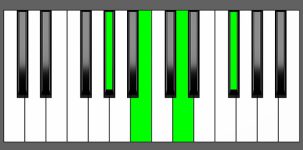
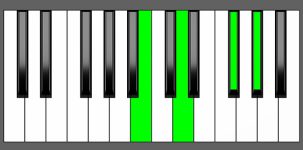
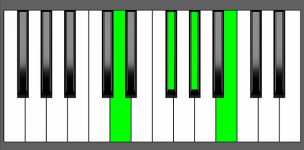
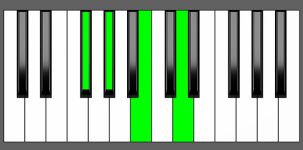
Piano Diagram of Abm7b5 in Root Position
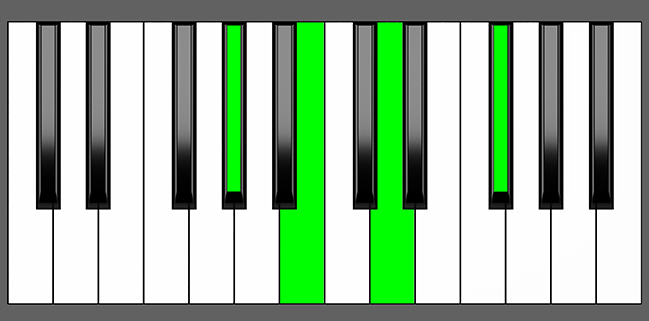
The Abm7b5 chord, also known as a half-diminished chord, is a minor dominant seventh chord with a flat 5th built on the Ab major scale. This chord consists of the root note Ab, the minor third Cb, the diminished fifth Ebb, and the minor seventh Gb.
Structure of Abm7b5
Notes |
|---|
| Ab, Cb, Ebb, Gb |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, m3, d5, m7 |
Abm7b5 Chord Inversions
The Abm7b5 chord has a total of 3 inversions:
| Root Position: | Ab | Cb | Ebb | Gb |
| 1st Inversion: | Cb | Ebb | Gb | Ab |
| 2nd Inversion: | Ebb | Gb | Ab | Cb |
| 3rd Inversion: | Gb | Ab | Cb | Ebb |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Abm7b5 Chord Equivalencies
When you invert a half-diminished chord to its first inversion, it becomes equivalent to a minor 6th chord built on its minor 3rd.
Let’s take the Abm7b5 chord which consists of the notes Ab, Cb, Ebb, Gb: its first inversion is Cb, Ebb, Gb, Ab, which is actually a Cb minor 6th chord (which is the enharmonic equivalent of B minor 6th).
1st Inversion of Abm7b5 = Bm6
Understanding the equivalencies of chords can be beneficial when playing or composing music. It can also help in analyzing and understanding the harmonic structure of a piece of music.
Music Theory and Harmony of Abm7b5
Abm7b5 is considered a half-diminished chord, which means it has a diminished fifth and a minor seventh interval. This chord can be used as a substitute for other chords, such as a dominant seventh chord or a minor chord.
In jazz and other styles of music, Abm7b5 is often used as a passing chord or as part of a ii-V-I progression. It can add tension and interest to a musical passage, and can also be used as a starting point for improvisation.
Before examining the most common use of this chord, let’s learn how to build it.
Building the Abm7b5 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the Ab Major Scale:
To form a minor 7b5 chord, you would typically include the root note, minor third, diminished fifth, and minor seventh from a minor scale.
However, when teaching this concept, it can be more effective to demonstrate its construction using a major scale. This is because a major scale better illustrates the relationship between intervals and their respective qualities.
So let’s take the Ab major scale:


To create an Abm7b5 chord, apply the formula R, m3, d5, m7 in the following manner:
- Begin with the Root note, Ab.
- Select the third interval, which is C. Then, subtract a half step to obtain the minor 3rd, Cb (B).
- Select the 5th interval, which is Eb then lower it by half step to get the diminished 5th, Ebb (D).
- Pick the 7th interval G, then lower it by a half step to get the minor 7th, Gb.
By following this simple formula, you can create a minor 7b5 chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals:
One method to create an Abm7b5 chord is by combining specific intervals – a minor 3rd, another minor 3rd, and a major 3rd.
m3 + m3 + 3 = m7b5 Chords
For example, to build an Abm7b5 chord:
- we start with the root note Ab.
- We then add a minor 3rd interval, which is three half-steps up from the root, to get B (Cb).
- Next, we add another minor 3rd interval, which is three half-steps up from B, to get D (Ebb).
- Finally, we add a major 3rd interval, which is four half-steps up from D, to get Gb.
Together, these intervals form the Abm7b5 chord.
How to Use Abm7b5 in a Chord Progression
The Abm7b5 chord is frequently used in ii-V-I progressions, where it functions as the ii chord. However, due to its versatile nature, it can also be used in various other musical contexts, such as:
- on natural minor and Major keys
- as a substitute for dominant 7th chords
- as a substitute for minor chords
Most common uses of Abm7b5
The Abm7b5 chord appears on the second scale degree (II) in the Gb natural minor scale and on the seventh scale degree (VII) in the A major scale.
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gb = F# | F# min7 | G#m7b5 = Abm7b5 | A Maj7 | B min7 | C# min7 | D Maj7 | E7 |
- Supertonic chord in F# minor as G#m7b5
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bbb = A | A Maj7 | B min7 | C# min7 | D Maj7 | E7 | F# min7 | G#m7b5 = Abm7b5 |
- Leading tone chord in A Major as G#m7b5
Abm7b5 as a Substitute for Dominant 7th Chords
Minor 7th flat 5th chords can replace dominant 7th chords when they share some of the same notes. A general rule of thumb when it comes to chord substitutions is that if the substitute chord contains at least the 3rd and 7th notes of the original chord, it’s often a viable option for substitution.
Bb7 ⇔ Abm7b5
E7 ⇔ Abm7b5
In this case, the Abm7b5 chord (Ab, Cb, Ebb, Gb) can serve as a substitute for Bb7 (Bb, D, F, Ab) and E7 (E, G#, B, D) due to their shared notes. Specifically, Abm7b5 shares the 7th and 3rd notes of Bb7 (which are Ab and D, respectively), as well as the 3rd and 7th notes of E7 (which are G# and D).
Rootless dominant 9th Chord Substitution
It’s worth noting that the substitution of E7 with Abm7b5 can also be viewed as a rootless dominant 9th chord substitution. This is because Abm7b5 contains the same essential notes as the E9 chord without the root note.
E9 = E (G#, B, D, F#)
Abm7b5 = Ab, Cb, Ebb, Gb
Abm7b5 as a Substitute for minor Chords
To replace a minor chord with an m7b5, build the m7b5 by taking the note three semitones lower than the original minor chord. So, in the case of a B minor chord, the m7b5 chord would be built three-half steps lower than the root note B.
On the ii Degree
| ii | V | I |
| B min7 | E7 | A Maj7 |
| Become | ||
| Abm7b5 | E7 | A Maj7 |
You can apply this substitution to a ii V I progression that has a B minor chord on the ii degree by replacing it with an Abm7b5 chord.
On the IV Degree
I IV iv I
| I | IV | iv | I |
| Gb Maj7 | B Maj7 | B min7 | Gb Maj7 |
| Become | |||
| Gb Maj7 | B Maj7 | Abm7b5 | Gb Maj7 |
Abm7b5 Chord Function in Major and Minor Keys
Understanding Scale Degrees
When we form chords from a scale, each note in the scale is given a specific degree that reflects its position within the scale. The degree of a note in a scale determines its function and the role it plays in the overall harmony of the music.
- Starting with the first degree of the scale, we have the Tonic chord. This chord serves as the foundation of the scale, providing a stable tonal center for the music. It’s like the “home base” of the music, and all melodies and harmonies are anchored to this chord.
- Moving on to the second degree, we have the Supertonic. This degree acts as a transitional note between the tonic and other notes in the scale, creating a sense of movement and flow in the melody or harmony.
- The third degree is the Mediant, which is located halfway between the tonic and dominant notes. This degree helps to establish whether the scale is major or minor and plays a critical role in determining the mood and emotional impact of the music.
- The fourth degree is the Subdominant, which complements the dominant and adds tension and resolution to the music. It creates a push-pull effect that keeps the listener engaged and interested.
- The fifth degree is the Dominant, which generates tension and a sense of expectation. It often acts as the climax of a musical phrase or section and is resolved by returning to the tonic.
- The sixth degree is the Submediant, which provides a sense of stability and restfulness to the music. It’s often used as a transition between the dominant and tonic, creating a feeling of calm and relaxation.
- Finally, we have the seventh degree, the Leading tone. This degree produces a strong sense of tension and a desire to resolve to the tonic. It’s often used to create a sense of resolution and completion in the melody or harmony.
Abm7b5 as Supertonic Chord in Gb minor
Abm7b5 as Leading Tone Chord in Bbb Major
Abm7b5 as Substitute for Bb7
Abm7b5 shares the 7th and 3rd notes of Bb7 so it’s possible to use an Abm7b5 in place of a Bb7 on the V degree. This is a common substitution used in jazz music and can add some interesting harmonic color to a progression.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 ⇒ Abm7b5 | C min7 | D m7b5 |
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| F min7 | Abm7b5 | Bb7 | Eb Maj7 |
I IV ii V iii vi ii V
| I | IV | ii | V | iii | vi | ii | V |
| Eb Maj7 | Ab Maj7 | F min7 | Bb7 | Abm7b5 | G min7 | Cmin7 | F min7 | Bb7 |
You can play the Abm7b5 chord by itself, or use it in combination with a Bb7 chord, either before or after the Abm7b5. This will allow you to explore the different tonal colors and tensions that each progression creates, and help you develop a stronger sense of how these chords can be used effectively in your musical compositions or improvisations.
Abm7b5 as Substitute for E7
Check G#m7b5 as Substitute for E7
Alternative Abm7b5 Nomenclature
- Abø
- Ab∅
- Lab ø
- Abm7b5
- Abm7°5
- Abm7b5
- Abm7/b5
- Abm7(-5)
- Abm7(b5)
- Ab 1/2dim
- Ab 1/2dim7
- Abm7 Flat 5
- Ab minor 7th b5
- Ab half-diminished
- Ab minor seventh flat fifth
Conclusion
The chord progressions and examples presented in this post provide a comprehensive overview of the most common uses of the Abm7b5 chord. It’s important to note, however, that there are many advanced harmony-related topics that could not be included due to space constraints. These topics include chord progressions built on harmonic and melodic scales, modal scales, hidden tonality, secondary dominants and other chord substitutions, non-functional harmony and atonal music, modal interchange and borrowed chords, voice leading and counterpoint, chromatisms, jazz harmony…I mean, music theory is a huge topic!
Although I couldn’t cover all of these topics in my post, I encourage readers to continue exploring these areas in their own study and research. By expanding your knowledge in these advanced areas of music theory, you can gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic possibilities that exist beyond the basics presented here.