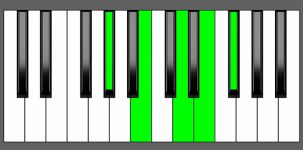
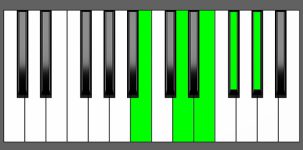
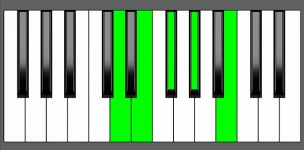
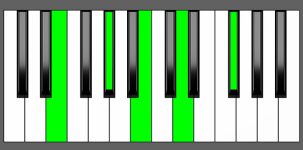
Piano Diagram of E9 in Root Position
An E9 chord is a dominant seventh chord built upon the key of E with an extra 9th note. The E9 chord can be used on the fifth degree of several scales as a variation of a dominant 7th chord. The 9th adds an extra layer of dissonance. Keep reading to understand the music theory behind this chord.
Structure of E9
Notes |
|---|
| E, G#, B, D, F# |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, 3, 5, m7, 9 |
Playing Extended Chords on Piano
Extended chords are commonly used in piano playing, but they can be tricky to play in their entirety due to the large number of notes involved. To make these chords more manageable, pianists often omit certain notes, such as the root or the 5th. Another technique is to split the chord between both hands, playing either full or partial chords in each hand.
However, even when notes are omitted or split between hands, extended chords can still create complex and dense harmonies. When these chords are inverted, the resulting clusters of notes can be particularly challenging to voice effectively.
E9 Chord Inversions
The E9 chord has a total of 4 inversions:
| Root Position: | E | G# | B | D | F# |
| 1st Inversion: | G# | B | D | E | F# |
| 2nd Inversion: | B | D | E | F# | G# |
| 3rd Inversion: | D | E | F# | G# | B |
| 4th Inversion: | F# | G# | B | D | E |
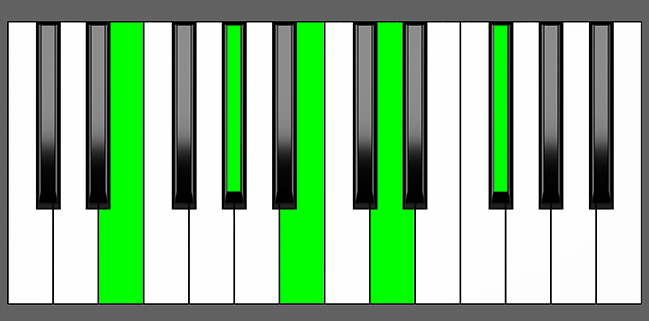
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Chord Inversion on Piano
Understanding chord inversions is an essential aspect of music theory as it helps to explain how chords are constructed and used in progressions. When playing chord inversions on a piano, it’s important to keep in mind that the diagrams used to illustrate the order of notes may not always be practical to play.
To achieve the proper chord voicings on a piano, you need to distribute the notes of the chord across various octaves and positions on the keyboard. This often means that the basic shape of the chord’s inversions shown in diagrams may not be the most convenient or comfortable way to play the chord.
While chord inversion diagrams can be useful in comprehending the structure and sequence of notes in a chord, it’s recommended to experiment with different voicings and fingerings to find the most efficient and comfortable way to play the chord while still preserving its intended harmonic function and sound.
Music Theory and Harmony of E9
The E9 chord is an extension of E7, which means you can add the 9th note to the E7 chord to create a unique and complex sound. You can use the E9 chord in all the positions where the E7 chord can be played. However, keep in mind that some positions may not work as well as others when using E9 instead of E7.
You may want to try out the E9 chord as an alternative to the E7 chord in different positions. Check out the E7 chord page for ideas on where to start experimenting. This will help you determine which positions work well with the E9 chord and which ones may not be as effective.
Building the E9 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the E Major Scale
To form an E9 chord, you combine the root (E), the major 3rd (G#), the 5th (B), the minor 7th (D), and the major 9th from the E scale (F#).


To create an E9 chord, apply the formula R, 3, 5, m7, 9 in the following manner:
- Begin with the Root note, which is E.
- Select the major 3rd interval, which is G#, and add it to the chord.
- Add the 5th interval, which is B.
- Add the minor 7th interval, which is the 7th (D#) less a half-step, D.
- Lastly, add the 9th, which is F#.
By following this simple formula, you can create a dominant 7th chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals
One method to create a dominant 7th chord is by combining specific intervals – a major 3rd, a minor 3rd, a minor 3rd, and a major 3rd.
3 + m3 + m3 + 3 = Dominant 9th Chords
For example, to create an E9 chord:
- we start with the root note E.
- We then add a major 3rd interval, which is four half-steps up from the root, to get G#.
- Next, we add a minor 3rd interval, which is three half-steps up from G#, to get B.
- We add another minor 3rd interval to get D and
- finally, we build a major 3rd from D and we end up with F#.
When we play these five notes together – E, G#, B, D, and F# – we get the E9 chord.
by Combining Chords
Another method to build dominant 9th chords is by combining a major triad with the minor chord built on its fifth note.
To create an E9 chord, for instance, you can combine an E Major triad with a B minor chord. These two chords share the note B, and when played together, they form an E9 chord.
E Major + B minor = E9
How to Use E9 in a Chord Progression
The E9 chord can be seen as an extension of the E7 chord and is often used in a similar way as a dominant 7th chord. In fact, the E7 chord contains the same notes (E, G#, B, D) except for the additional 9th note (F#) in the E9 chord.
Since the E9 chord includes the dominant 7th note (D), it has a similar function to the E7 chord in creating tension and preparing for the resolution to the tonic chord. Therefore, in most cases, the E9 chord can be used as a substitute for the E7 chord, and vice versa, depending on the desired musical context and sound.
These tables show the harmonized major and natural minor scale where you can find an E7 that can be replaced by an E9 but I suggest referring to the posts on dominant 7th chords to learn more fancy uses and contexts in which a dominant 9th chord can be played.
on A Major Scale
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A Maj7 | B min7 | C# min7 | D Maj7 | E7 ⇒ E9 | F# min7 | G#m7b5 |
- Dominant chord in A Major
on F# minor Scale
| Natural Minor | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F# | F# min7 | G#m7b5 | A Maj7 | B min7 | C# min7 | D Maj7 | E7 ⇒ E9 |
- Leading Tone chord in F# minor
E9 Chord Function in Major and Minor Keys
Understanding Scale Degrees
When we form chords from a scale, each note in the scale is given a specific degree that reflects its position within the scale. The degree of a note in a scale determines its function and the role it plays in the overall harmony of the music.
- Starting with the first degree of the scale, we have the Tonic chord. This chord serves as the foundation of the scale, providing a stable tonal center for the music. It’s like the “home base” of the music, and all melodies and harmonies are anchored to this chord.
- Moving on to the second degree, we have the Supertonic. This degree acts as a transitional note between the tonic and other notes in the scale, creating a sense of movement and flow in the melody or harmony.
- The third degree is the Mediant, which is located halfway between the tonic and dominant notes. This degree helps to establish whether the scale is major or minor and plays a critical role in determining the mood and emotional impact of the music.
- The fourth degree is the Subdominant, which complements the dominant and adds tension and resolution to the music. It creates a push-pull effect that keeps the listener engaged and interested.
- The fifth degree is the Dominant, which generates tension and a sense of expectation. It often acts as the climax of a musical phrase or section and is resolved by returning to the tonic.
- The sixth degree is the Submediant, which provides a sense of stability and restfulness to the music. It’s often used as a transition between the dominant and tonic, creating a feeling of calm and relaxation.
- Finally, we have the seventh degree, the Leading tone. This degree produces a strong sense of tension and a desire to resolve to the tonic. It’s often used to create a sense of resolution and completion in the melody or harmony.
E9 as Dominant Chord in A Major
In the A major scale, the E9 chord can be used as the dominant chord on the fifth degree of the scale. This means that the E9 chord would be the fifth chord in the scale and have a strong pull towards the tonic chord, which is the A major chord in this case.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| A Maj7 | Bmin7 | C# min7 | D Maj7 | E7 | F# min7 | G#m7b5 |
E9 Chord Progressions as V degree
Try playing these chord progressions to get an idea of how E9 functions as the dominant chord.
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| B min7 | E9 | E7 | A Maj7 |
I IV V
| I | IV | V |
| A Maj7 | D Maj7 | E9 | E7 |
I V vi IV
| I | V | vi | IV |
| A Maj7 | E9 | E7 | F# min 7 | D Maj7 |
I IV vi V
| I | IV | vi | V |
| A Maj7 | D Maj7 | F# min 7 | E9 | E7 |
Circle Progression
| I | IV | vii | iii | vi | ii | V | I |
| A Maj7 | D Maj7 | G#m7b5 | C# min7 | F#m7 | Bm7 | E9 | E7 | A Maj7 |
E9 as the Leading Tone chord in F# minor
In the F# minor scale, E9 could be a variation for the dominant 7th chord present on the VII degree.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| F# min7 | G#m7b5 | A Maj7 | B min7 | C# min7 | D Maj7 | E7 |
E9 as VII degree – Chord Progressions
These chord progressions can help you comprehend how E9 serves as the leading tone:
i iv VII i
| i | iv | VII | i |
| F# min7 | B min7 | E9 | E7 | F# min7 |
i VII VI V
| i | VII | VI | v |
| F# min7 | E9 | E7 | D Maj7 | C# min7 |
i III VII VI
| i | III | VII | VI |
| F# min7 | A Maj7 | E9 | E7 | D Maj7 |
i iv VII VI
| i | iv | VII | VI |
| F# min7 | B min7 | E9 | E7 | D Maj7 |
i iv VII III
| i | iv | VII | III |
| F# min7 | B min7 | E9 | E7 | A Maj7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| F# min7 | B min7 | E9 | E7 | A Maj7 | D Maj7 | G#m7b5 | C#7 | F# min7 |
Alternative E9 Nomenclature
- E 9
- Mi 9
- E 9th
- E 7/9
- E dom9
- E Ninth
- E Dominant 9
- E Dominant 9th
- E Dominant ninth
Conclusion
The chord progressions and examples presented in this post provide a comprehensive overview of the most common uses of the E9 chord. It’s important to note, however, that many advanced harmony-related topics could not be included due to space constraints.
I suggest referring to the posts on dominant 7th chords to learn more fancy uses and contexts in which a dominant 9th chord can be played.