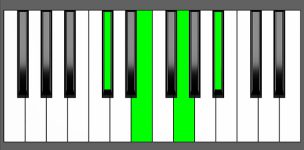
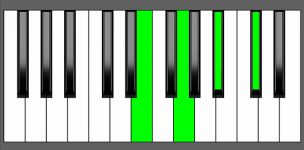
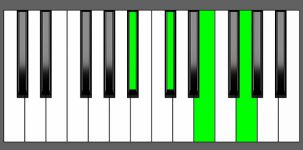
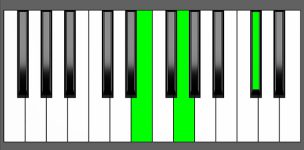
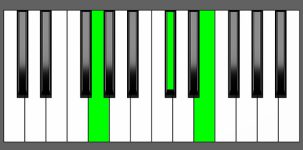
Piano Diagram of Db dim7 in Root Position
Db dim7 is a four-note chord that consists of a diminished triad (Db, Fb, Abb) with an added diminished 7th Cbb (Bb). In other words, it’s a stack of minor 3rd intervals on top of the Root note D-flat. Keep reading to learn more about the music theory behind this chord.
Structure of Db dim7
Notes |
|---|
| Db, Fb, Abb, Cbb |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, m3, d5, d7 |
Fingers Position
Left Hand |
|---|
| 5, 3, 2, 1
5, 4, 2, 1 |
Right Hand |
|---|
| 1, 2, 3, 4
1, 2, 3, 5 |
Db dim7 Chord Inversions
The Db dim7 chord has a total of 3 inversions:
| Root Position: | Db | Fb | Abb | Cbb |
| 1st Inversion: | Fb | Abb | Cbb | Db |
| 2nd Inversion: | Abb | Cbb | Db | Fb |
| 3rd Inversion: | Cbb | Db | Fb | Abb |
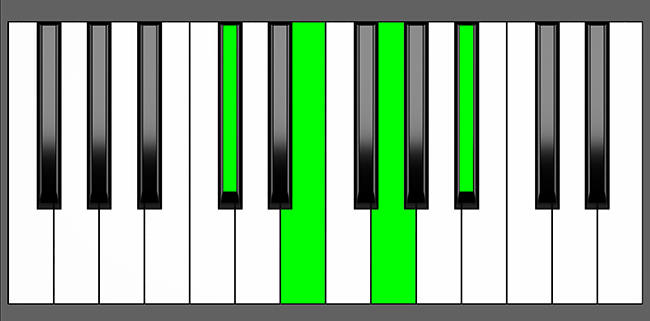
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Db dim7 Inversions Equivalences
Each note that makes up a Db dim7 chord can also be used as the root to create another diminished seventh chord. For example, if we start with a Db diminished seventh chord (Db, Fb, Abb, Cbb), we can change the starting note to Fb (E), Abb (G), or Cbb (Bb) to make a new diminished seventh chord with the same notes, just in a different order. Basically, all three inversions of a Db dim7 chord can be seen as separate diminished seventh chords. So we have:
Db dim7 = Fb dim7 = Abb dim7 = Cbb dim7
The reason each note in a Db dim7 chord can function as the root to create another diminished seventh chord is that the notes are all evenly spaced apart by intervals of a minor third. They have a symmetrical structure, meaning that each note is separated by the same distance of a minor 3rd interval. This means that when we start on any note in the chord and continue to stack minor thirds on top of it, we will always end up with the same four notes that make up a diminished seventh chord.
Db dim7 Root position = Db, Fb, Abb, Cbb
1st Inv. = E, G, Bb, Db = E dim7
2nd Inv. = G, Bb, Db, Fb = G dim7
3rd Inv. = Bb, Db, Fb, Abb = Bb dim7
If you try to build the diminished 7th chord of all keys, you’ll find that there are only three distinct dim7 chords that occur repeatedly, but with a different root note, covering all the keys.
| Distinct dim7 Chords | Notes | Root Position | Enharmonic Inversions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C dim7 | C – Eb – Gb – Bbb | C dim7 | D#/Eb dim7 |
F#/Gbdim7 |
A dim7 |
| D dim7 | D – F – Ab – Cb | D dim7 | F dim7 | G#/Ab dim7 |
B dim7 |
| E dim7 | E – G – Bb – Db | E dim7 | G dim7 | A#/Bb dim7 |
C#/Db dim7 |
As you can see, each of the three distinct chords represents a unique combination of four notes, and those four notes can be rearranged into four different inversions of the chord. By using these three distinct chords and their inversions, all 12 keys can be covered.
The choice of C, D, and E dim7 is just arbitrary, you can try to build all dim7 chords from another series of unique dim7 chords.
Music Theory and Harmony of Db dim7
The first section explains how to build a Db dim7 chord from the Db major scale or by combining minor thirds. The following sections discuss the characteristics and harmonic functions of the diminished seventh chord.
In particular, it covers how diminished 7th chords can be used as substitutes, passing chords, or variations for diminished triads, half-diminished, and dominant chords and how they can create tension and anticipation before resolving to more stable chords.
But first, let’s see how to build a Db dim7 chord.
Building the Db dim7 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the Db Major Scale
To build a diminished 7th chord, you need the Root, the minor 3rd, the diminished 5th, and the diminished 7th note. Let’s see how to do it starting from a major scale:


- Start from the root note, Db.
- Lower the major 3rd note by one half-step. In this case, the 3rd note on the Db major scale is an F. To get a minor 3rd interval, you need to lower it down to a natural E which we call Fb to preserve the basic interval structure of the chord.
- Lower the 5th note by one more half-step. Since the 5th note is an Ab, the diminished 5th is an Abb (G).
- Lower the 7th note by two additional half-steps*: the 7th interval on the Db major scale (C) is a major 7th interval. If you subtract a half step you get a minor 7th interval Cb (B). By lowering it down by another half step, you get the diminished 7th interval, Cbb (Bb).
- The resulting notes will form a diminished seventh chord with the formula R, m3, d5, and d7*.
*Note: In music theory, intervals like the minor 3rd and minor 7th are one half-step lower than their major counterparts. The diminished 5th interval is also one half-step lower than a perfect 5th, but for naming conventions it’s usually referred to as “diminished” instead of “minor” or “flat”. However, the diminished 7th interval is a little different. This is because the 7th interval can be major, minor, or diminished. To diminish a 7th interval, you need to subtract two half-steps from the major 7th interval, or one half-step from the minor 7th interval.
It’s easy to see that a diminished 7th interval is equivalent to a major 6th. Diminished 7th and major 6th intervals have the same pitch, even though they are named differently.
by Combining 3rds
Alternatively, a diminished 7th chord can be constructed by stacking three minor 3rd intervals on top of each other (a minor 3rd + a minor 3rd + a minor 3rd).
m3 + m3 + m3 = diminished 7th Chords
Let’s see how to build Db dim7:
Raise the root (Db) by a minor 3rd interval. This gives you the 3rd note of the chord which is E (Fb). Add another minor 3rd and you get a G (Abb). Finally, add another minor 3rd and you’ve completed the chord with the diminished 7th Bb (Cbb).
Characteristics of Diminished 7th Chords
Diminished 7th chords have a unique sound due to the combination of the first two minor 3rd intervals, creating a tritone interval. This interval spans six half-steps from the root note, and it has a dissonant sound that creates a feeling of instability or harshness.
Because of their dissonant sound, diminished 7th chords require resolution to a more consonant chord. They are commonly used in jazz and classical music genres to create tension and anticipation before resolving to a more stable chord.
How to Use Db dim7 in a Chord Progression
Diminished 7th chords are highly versatile and can effectively substitute diminished triads, half-diminished, and dominant chords. You can use them as intentional substitutes, passing chords, or variations.
Db dim7 as a Substitute for dim and m7b5 Chords
Diminished triads are considered “diatonic chords” as they naturally occur in the harmonization of both the natural minor and major scales. In contrast, diminished 7th chords are non-diatonic chords on natural minor and major scales because these scales produce half-diminished chords, which come with a major 7th.
For this reason, you could think that adding a diminished 7th note to a diminished triad may change the effect of the chord, but this is not true for diminished 7th chords.
When we look at the inversion of a diminished chord, we can observe a gap between the third and fifth notes in the first inversion, as well as between the fifth and root notes in the second inversion.
The addition of the diminished 7th note fills in these gaps without fundamentally changing the general feel of the chord. However, it does add a new note that can provide a strong sense of tension or dissonance, making the chord sound more full and rich.
The key concept to highlight is that a diminished 7th chord can effectively substitute a diminished triad without significantly altering the chord’s overall impact, despite being a non-diatonic chord for the presence of the diminished 7th interval.
The ratios between the intervals in a diminished 7th chord remain constant, regardless of which note is chosen as the root. Therefore, we can substitute a diminished 7th chord for a diminished triad or a half-diminished chord without altering its essential character.
The tables below show the B natural minor scale and its corresponding relative major scale, both of which contain a C# diminished chord (the enharmonic equivalent of Db dim7). It’s important to note that when we harmonize diminished triads, they result in a half-diminished chord. Therefore, these tables apply to both diminished triads and half-diminished chords.
The Db diminished chord can be found on the second scale degree (II) in the Cb natural minor scale and on the seventh scale degree (VII) in the Ebb Major scale. However, since these keys are theoretical, we can refer to its enharmonic equivalent keys B minor and D Major.
on Natural minor Scale
| Minor Scale | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cb = B | B min | C# dim ⇒ C# dim7 = Db dim7 | D Maj | E min | F# min | G Maj | A Maj |
- Supertonic chord in B minor as C# dim7
on Major Scale
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ebb = D | D Maj | E min | F# min | G Maj | A Maj | B min | C# dim ⇒ C# dim7 = Db dim7 |
- Leading tone chord in D Major as C# dim7
as a Substitute for Dominant 7th Chords
Diminished 7th chords can be used as substitutes for dominant 7th chords since they share some of the same notes.
For instance, let’s consider the Db diminished 7th chord (Db, Fb, Abb, Cbb). By lowering certain notes, we can obtain the following chords:
- Lowering the root, Db gives us a C7 chord (C, E, G, Bb).
- Lowering the E note results in an Eb7 (or D#7) chord (Eb, G, Bb, Db).
- Lowering the G note yields a Gb7 (or F#7) chord (Gb, Bb, Db, Fb).
- Similarly, lowering the Bb note produces an A7 chord (A, C#, E, G).
Given that Db dim7 is enharmonically equivalent to Fb (E) dim7, Abb (G) dim7, and Cbb (Bb) dim7, it can serve as a substitute for any dominant 7th chord with a root a half-step below any of these notes.
Thus, Db dim7 and its equivalent inversions can replace the following dominant 7th chords in a technique known as #Vdim7 substitution:
- C7 (root a half-step below Db)
- Eb7 or D#7 (root a half-step below E)
- Gb7 or F#7 (root a half-step below G)
- A7 (root a half-step below Bb)
As demonstrated in the table below, only three dim7th chords are needed to substitute for dominant 7th chords in all 12 keys:
| Distinct dim7th Chords | Notes | All 12 Dominant 7th Chords | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C dim7 | C – Eb – Gb – Bbb | B7 | D7 | F7 | Ab/G#7 |
| D dim7 | D – F – Ab – Cb | Db/C#7 | E7 | G7 | Bb/A#7 |
| E dim7 | E – G – Bb – Db | Eb/D#7 | Gb/F#7 | A7 | C7 |
Db dim7 as Supertonic Chord in Cb minor
Db dim7 as Leading Tone Chord in Ebb Major
Db dim7 as Passing Chord
Here are some tables that demonstrate how Db dim7 can be used as a passing chord in different keys. When we talk about a passing chord, we mean a chord that is temporarily inserted between two other chords to create a smooth and captivating harmonic progression.
Db dim7 as Passing Chord in Ab Major
I IV iii ii
| I | IV | IV°7 | iii | ii |
| Ab Maj7 | Db Maj7 | Db dim7 | C min7 | Bb min7 |
Db dim7 as Passing Chord in A Major
Db dim7 as Passing Chord in Db Major
I ii V
| I | I°7 | ii | V | |
| Db Maj7 | Db dim7 | Eb min7 | Ab7 | |
Db dim7 as Passing Chord in F minor
i vi v iv
| i | VI | VI°7 | v | iv |
| F min7 | Db Maj7 | Db dim7 | C min7 | Bb min7 |
Db dim7 as Passing Chord in Gb minor
Db dim7 as Passing Chord in Bb minor
i III iv V
| i | III | III°7 | iv | V |
| Bb min7 | Db Maj7 | Db dim7 | Eb min7 | F7 |
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulations
Db “dim7 chromatic modulation” refers to a chord progression where a diminished 7th chord is used to create chromatic movement in the harmony. This modulation technique involves incorporating a diminished 7th chord while transitioning from one chord to another, usually by moving in half steps. In the case of Db dim7, we can find both ascending and descending modulations like these:
| Maj or min | Db dim7 chord | Maj or min |
| C | Db dim7 | D |
| or | ||
| D | Db dim7 | C |
In a chromatic modulation, a diminished 7th chord serves as a pivot chord that connects two different chords. This chromatic modulation (C, Db, D or D, Db, C) can also be applied in various keys where a C chord is followed by a D chord:
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulation in Dbb Major
Check C# dim7 Chromatic Modulation in C Major
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulation in Abb (G)
Check C# dim7 Chromatic Modulation in G
i v iv VII in G minor
| i | v | bv°7 | iv | VII |
| G min7 | D min7 | Db dim7 | C min7 | F7 |
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulation in Bb Major
I iii ii V
| I | iii | biii°7 | ii | V |
| Bb Maj7 | D min7 | Db dim7 | C min7 | F7 |
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulation in Ebb minor
Check C# dim7 Chromatic Modulation in D minor
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulation in Bbb minor
Check C# dim7 Chromatic Modulation in A minor
Db dim7 Chromatic Modulation in Fb minor
Check C# dim7 Chromatic Modulation in E minor
Db dim7 as a Substitute for Dominant 7th Chords
Diminished 7th chords can replace dominant 7th chords because they share some of the same notes. However, since all inversions of a dim7 chord are themselves dim7 chords with different names but same notes, any inversion of Db dim7 can also be used as a substitute for the V degree.
In this case, I recommend referring to the C# dim7 chord instead of its enharmonic equivalent, Db dim7. The reason for this suggestion is that Db dim7 is less commonly used due to the abundance of accidentals involved. By opting for C# dim7, which has a simpler and more commonly recognized notation
Db dim7 as a Substitute for Dbb7 in Gbb
Check C# dim7 as a Substitute for C7 in F
Db dim7 as a Substitute for Eb7 in Ab or D#7 in G#
In the key of Ab major, an alternative option for replacing the Eb7 chord is to utilize the Db dim7 chord as an inversion of the #V°7, which is E dim7 in this particular context.
II #V°7 I in Ab Major and Ab or G# minor
| ii | V ⇒ #V°7 | I |
| Bb min7 | Eb7 ⇒ Edim7 = Dbdim7 | Ab Maj7 |
| iiø | V ⇒ #V°7 | i |
| Bbm7b5 | Eb7 ⇒ Edim7 = Dbdim7 | Ab min7 |
| A#m7b5 | D#7 ⇒ Edim7 = Dbdim7 | G# min7 |
IV #V°7 I in Ab Major and Ab or G# minor
| IV | #V°7 | I |
| Db Maj7 | Edim7 = Dbdim7 | Ab Maj7 |
| iv | #V°7 | i |
| Db min7 | Edim7 = Dbdim7 | Ab min7 |
| C# min7 | Edim7 = Dbdim7 | G# min7 |
I #V°7 VI IV in Ab Major and Ab or G# minor
| I | V | vi | #V°7 |
| Ab Maj7 | Eb7 | F min7 | Edim7 = Dbdim7 |
| i | v | VI | #V°7 |
| Ab min7 | Eb min7 | E Maj7 | Edim7 = Dbdim7 |
| G# min7 | D# min7 | E Maj7 | Edim7 = Dbdim7 |
Db dim7 as a Substitute for Gb7 in B
In both B major and B minor, you can use a Db dim7 chord instead of a Gb7 chord. This works because Db dim7 shares common notes with Gb7 (Gb, Bb, Db, Fb), specifically Db, Fb, and Cbb (Bb).
Here are some chord progressions in major and minor keys where you can replace a Gb7 chord with a Db dim7 chord. The Db dim7 chord acts as an inversion of the #V°7 chord G dim7.
II #V°7 I in B Major and B minor
| ii | V ⇒ #V°7 | I |
| C# min7 | F#7 ⇒ Gdim7 = Dbdim7 | B Maj7 |
| ii | V ⇒ #V°7 | i |
| C#m7b5 | F#7 ⇒ Gdim7 = Dbdim7 | B min7 |
When considering the substitution of Db dim7 for F#7 in both B major and B minor in a II-V-I progression, it’s important to note that this may not be the optimal choice due to the shared root between the II chord C#m7b5 (same as Dbm7b5) and the inversion of the #V°7 chord (Db dim7). However, it remains a viable option worth exploring.
I IV #V°7 I in B Major and B minor
| I | IV | #V°7 | I |
| B Maj7 | E Maj7 | Gdim7 = Db dim7 | B Maj7 |
| i | iv | #V°7 | i |
| B min7 | E min7 | Gdim7 = Db dim7 | B min7 |
I #V°7 VI IV in B Major and B minor
| I | #V°7 | vi | IV | V |
| B Maj7 | Gdim7 = Dbdim7 | G# min7 | E Maj7 | F#7 |
| i | #V°7 | VI | iv | V |
| B min7 | Gdim7 = Dbdim7 | G Maj7 | E min7 | F#7 |
Db dim7 as a Substitute for A7 in D
Db dim7 can function as a substitute for A7 in both D major and D minor. This substitution is possible because Db dim7 shares common tones with A7, specifically Db (C#), Fb (E), and Abb (G).
The tables below showcase chord progressions in major and minor keys where you can replace an A7 with a Db dim7, which serves as an inversion of the #V°7 chord Bb dim7.
II #V°7 I in D Major and D minor
| ii | V ⇒ #V°7 | I |
| E min7 | A7 ⇒ Bbdim7 = Db dim7 | D Maj7 |
| ii | V ⇒ #V°7 | i |
| Em7b5 | A7 ⇒ Bbdim7 = Db dim7 | D min7 |
I IV #V°7 I in D Major and D minor
| I | IV | #V°7 | I |
| D Maj7 | G Maj7 | Bbdim7 = Db dim7 | D Maj7 |
| i | iv | #V°7 | i |
| D min7 | G min7 | Bbdim7 = Db dim7 | D min7 |
I #V°7 VI IV in D Major and D minor
| I | #V°7 | vi | IV |
| D Maj7 | Bbdim7 = Db dim7 | B min7 | G Maj7 |
| i | #V°7 | VI | iv |
| D min7 | Bbdim7 = Db dim7 | Bb Maj7 | G min7 |
Db dim as a Substitution for a Secondary Dominant A7
In the key of G (major or minor), the Db diminished 7th chord (Db dim7) can serve as a substitution for the secondary dominant A7.
Secondary dominants are chords in traditional harmony that temporarily establish a new tonal center within a piece of music. They typically function as dominant chords of a key other than the tonic. In the key of G major, the secondary dominant A7 would normally resolve to D major. In this particular case, it resolves on a D7, which is the fifth degree of G, and then resolves further to the tonic.
The Db dim7 chord creates tension and can resolve effectively to D7, similar to how the A7 chord would resolve.
bV°7 V I in G Major and G minor
| V7/V ⇒ bV°7 | V | I |
| A7 ⇒ Db dim7 | D7 | G Maj7 or G min7 |
Alternative Names for Db dim7
- Db diminished 7th
- Dbdim7
- Db°7
Conclusion
The chord progressions and examples presented in this post provide a comprehensive overview of the most common uses of the Db dim7 chord. It’s important to note, however, that many advanced harmony-related topics could not be included due to space constraints. These topics include chord progressions built on harmonic and melodic scales, modal scales, hidden tonality, secondary dominants and other chord substitutions, non-functional harmony and atonal music, modal interchange and borrowed chords, voice leading and counterpoint, chromatisms, jazz harmony…I mean, music theory is a huge topic!
Although I couldn’t cover all of these topics in my post, I encourage readers to continue exploring these areas in their own study and research. By expanding your knowledge in these advanced areas of music theory, you can gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic possibilities that exist beyond the basics presented here.