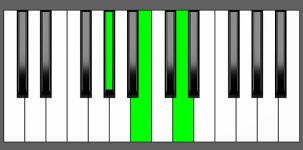
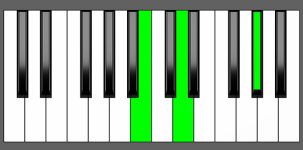
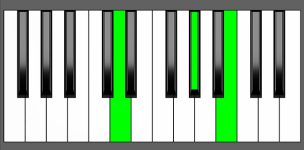
Piano Diagram of Ab dim in Root Position
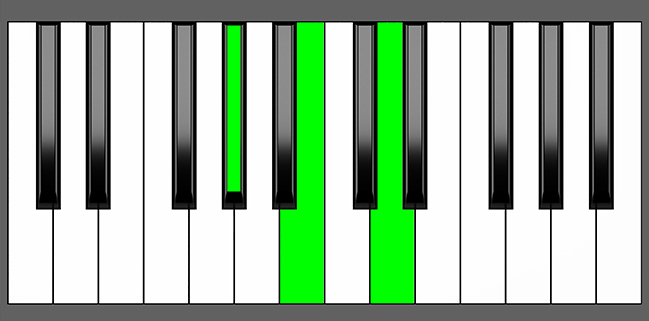
The Ab dim chord is the diminished triad built upon the A-flat key. It is built by combining the Root note (Ab), the minor 3rd (Cb), and the diminished 5th (Ebb) notes from the Ab scale. Keep reading to learn more about the music theory behind this chord.
Structure of Ab dim
Notes |
|---|
| Ab, Cb, Ebb |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, m3, d5 |
Fingers Position
Left Hand |
|---|
| 4, 2, 1
5, 3, 1 |
Right Hand |
|---|
| 1, 2, 4
1, 3, 5 |
Ab dim Chord Inversions
The Ab dim chord has a total of 2 inversions:
| Root Position: | Ab | Cb | Ebb |
| 1st Inversion: | Cb | Ebb | Ab |
| 2nd Inversion: | Ebb | Ab | Cb |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Music Theory and Harmony of Ab diminished
What are Diminished Chords?
In music theory, diminished chords are classified as triads just like major, minor, and augmented chords. A diminished triad is a chord that has a root note, a minor 3rd, and a diminished 5th. They are often abbreviated with a small circle (°) or the letters “dim”. For example, an A-diminished chord would be written as A° or Adim.
The interval between the root and the diminished 5th is called a “tritone” interval and creates a dissonant sound that adds tension and instability. Diminished triads are commonly used as transitional chords, leading to more stable chords.
Different types of Diminished Chords
- Diminished triads are usually considered unstable and are often used as transitional chords that create tension and lead to a more stable chord.
- There are also diminished seventh chords, which include an added diminished seventh interval above the root note. These chords are often written as °7 or dim7. They can also be used as a substitute for dominant 7th chords.
- Additionally, there are half-diminished chords (also known as minor seventh flat five chords), which include a minor seventh interval instead of a diminished seventh.
But for now, let’s explore the simpler diminished triad in the key of Ab.
Building the Ab dim Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from a Major Chord
The formula for a diminished chord is R, m3, d*5.
*The diminished 5th is one half-step lower than a perfect 5th. It’s called “diminished” instead of “minor” just for naming conventions.


To build a diminished chord, you begin by selecting the root note, the 3rd note, and the 5th note of the major scale. Next, you lower the 3rd and the 5th note by one half-step.
So, if you want to build an Ab diminished chord, you would start with the Ab major chord, which consists of the notes Ab, C, and Eb. Then, you would lower the third note, C, by one half-step to get B (which we call Cb to keep the basic chord structure) and lower the fifth note, Eb, by one more half-step to get D (as before, we call it Ebb to preserve the chord structure).
The resulting notes, Ab, Cb, and Ebb, form the Ab diminished chord.
by Combining 3rds
Alternatively, a diminished chord can be built by stacking two minor 3rd intervals on top of each other. To get this chord, you begin with the root note and then raise it by a minor 3rd. Next, you raise the third note by another minor 3rd. The resulting chord will consist of three notes that are spaced an equal distance apart.
m3 + m3 = diminished Chords
To form an Ab dim chord, you start with the root note Ab and raise it by a minor 3rd to B (Cb). Then, you raise the third note by another minor 3rd to D (Ebb). This results in an Ab dim chord consisting of the notes Ab, Cb, and Ebb.
Ab dim in a Chord Progression
The tables below display the enharmonic equivalent keys for the Gb minor scale and its relative major scale, which are theoretical keys that include an Ab diminished chord. In the Gb minor scale, the Db diminished chord is found on the second scale degree (II), while in the Bbb major scale, it is found on the seventh scale degree (VII). Due to the high number of accidentals in these keys, it is more practical to refer to their enharmonic equivalent keys, F# and A using the enharmonic equivalent chord of Ab dim and G# dim.
However, for a more comprehensive list of the uses of the Gb diminished chord, please refer to the dim7 tables, where I discuss some of the features of these chords in greater detail.
on Natural minor Scale
| Minor Scale | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gb = F# | F# min | G# dim = Ab dim | A Maj | B min | C# min | D Maj | E Maj |
- Supertonic chord in F# minor as G# dim
on Major Scale
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bbb = A | A Maj | B min | C# min | D Maj | E Maj | F# min | G# dim = Ab dim |
- Leading tone chord in A Major as G# dim
Ab dim in Gb Minor
Check G# dim in F# Minor
Ab dim in Bbb Major
Check G# dim in A Major
Alternative Names for Ab Diminished
- Ab°
- Abdim
- Ab diminished
- A-flat diminished