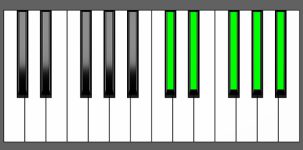
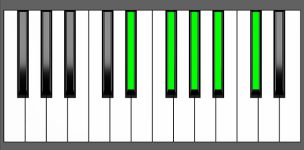
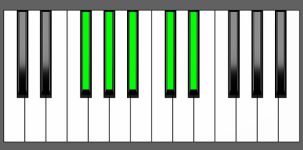
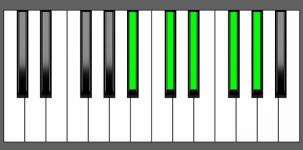
Piano Diagram of Ab9sus4 in Root Position
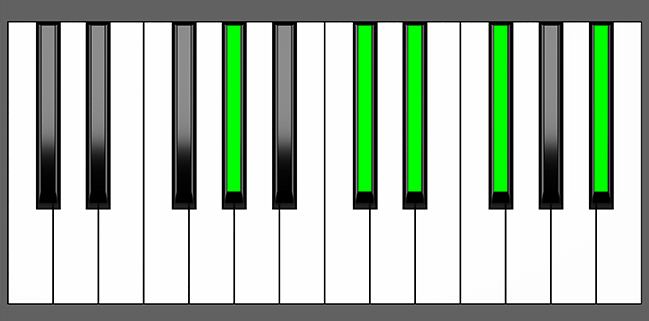
The Ab9sus4 chord is a suspended dominant 9th chord built upon the key of Ab. It’s made by the root note Ab, the perfect 4th Db, the perfect 5th Eb, the minor 7th Gb, and the major 9th Bb. Keep reading to gain a deeper understanding of the music theory behind this chord.
Structure of Ab9sus4
Notes |
|---|
| Ab, Db, Eb, Gb, Bb |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, 4, 5, m7, 9 |
How to play an Ab9sus4
You can start by playing the root note Ab with your left hand. Then, with your right hand, you can play the 4th Db, the minor 7th Gb, and the 9th note Bb. You can add the 5th, Eb, to get a little bit of dissonance.
Ab + (Db, Gb, Bb)
This will result in a simplified Ab9sus4 chord that consists of the root note, perfect 4th, minor 7th, and the 9th notes only.
Another simple way to voice this chord is to play the root note with your left hand and an Eb min7 chord with your right hand.
Ab + Ebm7 =
Ab + (Eb, Gb, Bb, Db) =
Ab9sus4
This voicing is essentially the second inversion of a 9sus4 chord without the root note, which is equivalent in sound to a minor 7th chord built on the 5th note from the root.
Ab9sus4 Chord Inversions
The Ab9sus4 chord has a total of 4 inversions:
| Root Position: | Ab | Db | Eb | Gb | Bb |
| 1st Inversion: | Db | Eb | Gb | Ab | Bb |
| 2nd Inversion: | Eb | Gb | Ab | Bb | Db |
| 3rd Inversion: | Gb | Ab | Bb | Db | Eb |
| 4th Inversion: | Bb | Db | Eb | Gb | Ab |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams

Chord Inversions on Piano
While chord inversions are a fundamental concept in music theory, the diagrams that show the sequence of notes in a complex chord on a piano keyboard may not necessarily be practical for playing. This is because proper chord voicings involve distributing the notes of the chord across different octaves and positions on the keyboard. This can be very different from the basic shape of the chord’s inversions. Therefore, the diagrams of chord inversions are mainly intended to show the sequence of notes on the piano keyboard for music theory purposes, rather than for practical playing.
Music Theory and Harmony of Ab9sus4
What are Suspended Chords?
Suspended chords are a type of chord where the third note is replaced by either a major second or a perfect fourth. This creates sus2 and sus4 chords, which have a unique and sometimes unresolved sound that adds tension and interest to music. These chords can be used as substitutes for major and minor chords because of their neutral nature.
The 9sus4 chord is a more intricate version of the sus4 chord, featuring a minor 7th and 9th note in addition to the perfect fourth. This chord is commonly used in jazz and blues music to add complexity and interest to chord progressions. It is often used as a substitute for dominant 7th chords. Read on to learn how to build an Ab9sus4 chord, or scroll down to see where it can be used in different keys and degrees.
Building the Ab9sus4 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from a Major Scale
To create a 9sus4 chord, you can use the Major scale as a reference by combining a Root, a 4th, a 5th, a minor 7th, and a 9th.
In this case, to build an Ab9sus4 let’s start from the Ab Major scale, which includes the notes Ab, Bb, C, Db, Eb, F, and G.


Apply the formula R, 4°, 5°, m7°, 9° to get an Ab9sus4 chord.
- Select the Root note, Ab.
- Pick the 4th note, Db.
- Add the 5th note, which is Eb.
- To add the 7th note, we need to use a minor 7th interval, which means we must use a minor seventh. In the Ab Major scale, the 7th note is G, so the minor 7th is natural Gb.
- Lastly, include the 9th note of the Ab Major scale, which is Bb.
by Combining Intervals
To build a 9sus4 chord, you can stack together a perfect 4th, a whole-tone (or major 2nd), a minor 3rd, and a major 3rd.
4 + 2 + m3 + 3 = 9sus4 Chords
In fact, when building an Ab9sus4 chord, you can see that Ab-Db is a perfect 4th, Db-Eb is a major 2nd, Eb-Gb is a minor 3rd, and Gb-Bb is a major 3rd.
How to Use Ab9sus4 in a Chord Progression
Suspended chords have a unique quality that sets them apart from major and minor chords. They are neither major nor minor, which makes them a useful tool for creating tension and suspense in a musical composition before resolving to a stable major or minor chord.
To use an Ab9sus4 chord in a chord progression, you can refer to the following tables, which show the most common positions where the chord can be found or used. However, it’s important to note that, since this chord features a minor 7th, it cannot be used with Maj7 chords, such as sus2 or sus4 chords. Nonetheless, it can be used on dominant chords and in all positions where an Ab min7 is present.
Ab9sus4 as Substitute of Ab7
Ab9sus4 can be used as a substitute for Ab7 in major and minor keys. In Db major, Ab7 can be replaced with Ab9sus4 in the V position. Similarly, in the Bb minor key, Ab7 can be substituted with Ab9sus4 in the VII position.
on Major Scales
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Db | Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 ⇒ Ab9sus4 | Bb min7 | Cm7b5 |
- Dominant chord in Db Major
on Natural minor Scales
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bb | Bb min7 | Cm7b5 | Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 ⇒ Ab9sus4 |
- Leading tone chord in Bb minor
Ab9sus4 as Substitute of Ab min7
Ab9sus4 chord can be used as a substitute for Ab minor chords in various major and minor keys. Note that in the key of E Major and Db minor, Bb can clash with the A notes that are part of those keys. While this doesn’t prevent you from using the Ab9sus4 chord in those positions, it’s important to be aware that it can create a strong dissonance with the melody or other elements of the composition.
on Major Scales
| Major Scales | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gb | Gb Maj7 | Abm7 ⇒ Ab9sus4 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 | Eb min7 | Fm7b5 |
| Fb = E | E Maj7 | F# min7 | G#m7 ⇒ G#9sus4 = Ab9sus4 | A Maj7 | B7 | C# min7 | D#m7b5 |
| Cb = B | B Maj7 | C# min7 | D# min7 | E Maj7 | F#7 | G#m7 ⇒ G#9sus4 = Ab9sus4 | A#m7b5 |
- Supertonic chord in Gb Major
- Non Diatonic Mediant chord in E Major as G#9sus4
- Submediant chord in B Major as G#9sus4
on Natural minor Scales
| Minor Scales | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ab | Abm7 ⇒ Ab9sus4 | Bbm7b5 | Cb Maj7 | Db min7 | Eb min7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
| Eb | Eb min7 | Fm7b5 | Gb Maj7 | Abm7 ⇒ Ab9sus4 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
| Db = C# | C# min7 | D#m7b5 | E Maj7 | F# min7 | G#m7 ⇒ G#9sus4 = Ab9sus4 | A Maj7 | B7 |
- Tonic chord in Ab minor
- Subdominant chord in Eb minor
- Non Diatonic Dominant chord in Db minor as G#9sus4
Ab9sus4 Chord Function in Major and Minor Keys
Understanding Scale Degrees
When creating chords from a scale, each note in the scale is assigned a degree, which reflects its position in the scale. In the diatonic major scale, there are seven degrees, and each degree has a unique role in the overall harmony of the scale.
- The first degree of the scale is called the Tonic, and it serves as the foundation for the scale. It provides a stable tonal center and is often referred to as the “home base” of the music.
- The second degree of the scale is called the Supertonic. It’s typically used as a passing note between the tonic and other scale degrees, and it adds a sense of movement to the melody or harmony.
- The third degree of the scale is called the Mediant. It’s located halfway between the tonic and dominant notes and helps to establish whether the scale is major or minor.
- The fourth degree of the scale is called the Subdominant. It’s often used as a complementary harmony to the dominant and adds a sense of tension and resolution to the music.
- The fifth degree of the scale is called the Dominant. It generates tension and a sense of expectation, and it’s typically resolved by returning to the tonic.
- The sixth degree of the scale is called the Submediant. It’s often utilized as a transition between the dominant and tonic, and it provides a sense of stability and restfulness to the music.
- The seventh degree of the scale is called the Leading tone. It’s located one half step below the tonic and produces a strong sense of tension and a desire to resolve to the tonic. It’s often used to create a sense of resolution and finality in the melody or harmony.
Ab9sus4 in Db Major
When playing in the key of Db Major, the fifth degree of the scale is Ab7. However, substituting it with an Ab9sus4 chord can introduce a feeling of anticipation and suspense, which can be resolved by returning to the dominant chord or by moving to another degree of the scale.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 | Bb min7 | Cm7b5 |
Ab9sus4 as V degree – Chord Progressions
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| Eb min7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 | Db Maj7 |
You can experiment with different ways of playing the Ab9sus4 chord in the key of Db Major. For example, you could play just the Ab9sus4 chord, or split the measure in half and play both the Ab9sus4 and Ab7 chords. Another option is to invert the order of the chords, playing the Ab7 chord first and then resolving to the Ab9sus4 chord.
I IV V
| I | IV | V |
| Db Maj7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 |
I V vi IV
| I | V | vi | IV |
| Db Maj7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 | Bb min7 | Gb Maj7 |
I IV vi V
| I | IV | vi | V |
| Db Maj7 | Gb Maj7 | Bb min7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 |
I IV ii V iii vi ii V
| I | IV | ii | V | iii | vi | ii | V |
| Db Maj7 | Gb Maj7 | Eb min7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 | F min7 | Bb min7 | Eb min7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 |
Ab9sus4 in Bb Minor
In the Bb minor key, the seventh degree of the scale features an Ab7 chord. By incorporating an Ab9sus4 chord in this position, you can generate a feeling of expectation and tension, which prepares the listener for the eventual resolution to the tonic chord. You can experiment with playing just the Ab9sus4 chord or combining it with the Ab7 chord.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| Bb min7 | Cm7b5 | Db Maj7 | Eb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 |
Ab9sus4 as VII degree – Chord Progressions
i VI VII
| i | V | VII |
| Bb min7 | F min7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 |
i v VI VII
| i | v | VI | VII |
| Bb min7 | F min7 | Gb Maj7 | Ab7 | Ab9sus4 |
i III VII VI
| i | III | VII | VI |
| Bb min7 | Db Maj7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 | Gb Maj7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| Bb min7 | Eb min7 | Ab9sus4 | Ab7 | Db Maj7 | Gb Maj7 | Cm7b5 | F7 | Bb min7 |
Ab9sus4 in Gb Major
In Gb Major key, the second chord of the scale is typically an Ab minor. However, substituting it with an Ab9sus4 chord can introduce some color and tonal intrigue to a chord progression.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| Gb Maj7 | Ab min7 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 | Eb min7 | Fm7b5 |
Ab9sus4 Chord Progressions as ii degree
ii V I
| ii | V | I |
| Ab9sus4 | Abm7 | Db7 | Gb Maj7 |
I IV ii V iii vi ii V
| I | IV | ii | V | iii | vi | ii | V |
| Gb Maj7 | Cb Maj7 | Ab9sus4 | Abm7 | Db7 | Bb min7 | Eb min7 | Abm7 | Ab9sus4 | Db7 |
Ab9sus4 in Fb Major (Non Diatonic)
Check G#9sus4 in E Major
Ab9sus4 in Cb Major
Check G#9sus4 in B Major
Ab9sus4 in Ab Minor
In the key of Ab minor, incorporating the Ab9sus4 chord can add variation to the traditional Abm chord typically used in the key.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| Ab min7 | Bbm7b5 | Cb Maj7 | Db min7 | Eb min7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
Ab9sus4 Chord Progressions as i degree
i VI VII
| i | VI | VII |
| Ab9sus4 | Abm7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
i iv VI VII
| i | iv | VI | VII |
| Ab9sus4 | Db min7 | Fb Maj7 | Gb7 |
Ab9sus4 in Eb Minor
When playing in the key of Eb minor, you can try using the Ab9sus4 chord as a substitution or variation for the Ab major chord on the IV degree.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| Eb min7 | Fm7b5 | Gb Maj7 | Ab min7 | Bb min7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
Ab9sus4 Chord Progressions as iv degree
iv III VI VII
| iv | III | VI | VII |
| Ab9sus4 | Abm7 | Gb Maj7 | Cb Maj7 | Db7 |
i iv VI v
| i | iv | VI | v |
| Eb min7 | Ab9sus4 | Abm7 | Cb Maj7 | Bb min7 |
Ab9sus4 in Db Minor (Non Diatonic)
Check G#9sus4 in C# minor
9sus4 and 11th Chords: Similarities and Differences
9sus4 chords share almost the same notes as 11th chords. The only difference is the presence of the 3rd in 11th chords.
Ab9sus4 = Ab, Db, Eb, Gb, Bb
Ab11 = Ab, C, Eb, Gb, Bb, Db
However, it is important to note that a 4th is not the same as an 11th, even if they are the same note. There is an octave of difference between them. This distinction may not matter when playing an inversion of the chord, but it is still important to be aware of.
Alternative Ab9sus4 Chord Nomenclature
- Ab9 sus4
- Ab7(9sus4)
- Ab9sus 4th
- Ab nine suspended 4th
- Ab ninth suspended fourth
- Ab Dominant ninth suspended 4