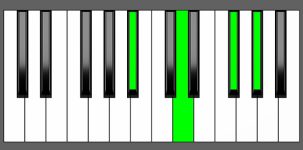
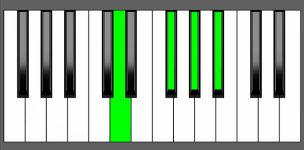
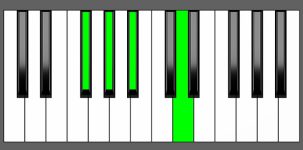
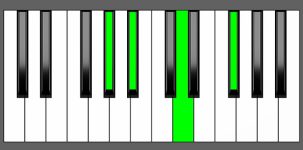
Piano Diagram of A#7#5 in Root Position

An A#7#5 chord is an altered dominant seventh chord that is built upon the key of A#. This chord consists of the root note A#, the major third Cx, the augmented fifth Ex (which is equivalent to F#), and the minor seventh G#. However, due to the dissonance created by the augmented triad, the A#7#5 chord can be used as a substitute for dominant chords only in specific musical contexts. Another common use of this chord is as part of a modulation to or from an A#7 chord. If you keep reading, you will learn more about the music theory that underpins this chord.
Structure of A#7#5
Notes |
|---|
| A#, Cx, Ex, G# |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, 3, #5, m7 |
Fingers Position
Left Hand |
|---|
| 5, 3, 2, 1 |
Right Hand |
|---|
| 1, 2, 4, 5 |
How to play an A#7#5
To play an A#7#5 chord, you can use the following voicing: begin by playing the root note A# with your left hand. Then, with your right hand, play the notes G# (minor 7th), Cx (major 3rd), and Ex (F#, the sharp 5th).
A# + G#, Cx, Ex
This will result in a voicing of A#7#5 that includes all notes: the root note, major 3rd, minor 7th, and sharp 5th.
A#7#5 Chord Inversions
The A#7#5 chord has a total of 3 inversions:
| Root Position: | A# | Cx | Ex | G# |
| 1st Inversion: | Cx | Ex | G# | A# |
| 2nd Inversion: | Ex | G# | A# | Cx |
| 3rd Inversion: | G# | A# | Cx | Ex |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Chord Inversions on Piano
A solid grasp of chord inversions is essential in music theory as it provides insights into how chords are built. When playing chord inversions on a piano, it’s crucial to realize that the charts depicting the note order may not always be practical or playable.
To achieve the correct chord voicings on a piano, you need to distribute the chord notes across different octaves and positions on the keyboard. This often involves deviating from the standard shape of the chord’s inversions presented in charts, which may not be the most practical or comfortable way to play the chord.
While chord inversion charts are useful for understanding the structure and sequence of notes in a chord, it’s advisable to experiment with different voicings and fingerings to discover the most efficient and comfortable way to play the chord, while still maintaining its intended harmonic function and sound.
Music Theory and Harmony of A#7#5
Dominant 7#5 chords are often used as a transitional chord to add an extra layer of tension to a dominant 7th chord and prepare for the resolution to the tonic. The A#7#5 chord can substitute or enhance the A#7 chord, commonly on the V degree, but also on the III degree, and occasionally on other degrees as a secondary dominant chord.
Before examining the most common use of this chord, let’s learn how to build it.
Building the A#7#5 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the A# Major Scale:
To form an A#7#5 chord, you combine the root (A#), the major 3rd (Cx), the augmented 5th (Ex), and the minor 7th (G#) from the A# scale.


To create an A#7#5 chord, apply the formula R, 3, #5, m7 in the following manner:
- Begin with the Root note, A#.
- Select the major 3rd interval, which is Cx.
- Add the 5th interval, which is E# then raise it by half step: Ex (which is equivalent to an F#).
- Add the minor 7th interval, G#.
By following this simple formula, you can create a 7#5 chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals:
One method to create a 7#5 chord is by combining specific intervals – a major 3rd, a major 3rd, and a 2nd.
3 + 3 + 2 = 7#5 Chords
For example, to build an A#7#5 chord:
- we start with the root note A#.
- We then add a major 3rd interval, which is four half-steps up from the root, to get Cx.
- Next, we add another major 3rd interval, which is again four half-steps up from Cx (D), to get Ex (F#).
- Finally, we add a 2nd interval, which is two half-steps up from Ex, to get G#.
Together, these intervals form the A#7#5 chord.
How to Use A#7#5 in a Chord Progression
The A#7#5 can work as a substitute or as a passing chord to an A#7 that can be found in major and natural minor scales. However, note that it’s a non-diatonic chord due to the presence of the augmented 5th.
These tables show the harmonized major and natural minor scales where you can find an A#7 or use it in place of other chords.
Most common uses of A#7#5
A#7#5 in D# Major and D# minor
The A#7#5 chord is a popular choice for creating tension in music, often functioning as a dominant chord. In the context of the key of D# major, you can use A#7#5 as the V7 chord, setting the stage for a resolution back to the I chord (D# major).
However, D# major is a theoretical key, so in this case, it’s more practical to refer to its enharmonic equivalent key Eb major.
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D# = Eb | Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 ⇒ Bb7#5 = A#7#5 | C min7 | Dm7b5 |
- Substitute or Passing Chord to the Dominant chord in Eb Major as Bb7#5
A#7#5 as Substitute for A# min7
The A#7 chord, taken from the harmonic minor scale, is frequently chosen to substitute for an A# min7 chord in the key of D# minor. In certain situations, you can also opt for the A#7#5 chord instead of the A#7 chord, intensifying the harmonic tension and guiding the progression towards the D# min7 chord.
| Minor Scale | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D# | D# min7 | E#m7b5 | F# Maj7 | G# min7 | A#m7 ⇒ A#7 ⇒ A#7#5 | B Maj7 | C#7 |
- Substitute or Passing Chord to the Dominant chord in D# minor
A#7#5 in a I – III7 Progression
The A#7#5 chord is frequently employed as a substitute for the III degree in a I – III7 chord progression. This progression typically involves an A# minor chord, but when using the chords F# Maj7 (I) and A#7 (III7), you can introduce the A#7#5 chord instead of the usual A# minor chord.
The A#7#5 chord contributes a distinctively dissonant augmented triad, adding a unique flavor to the progression.
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F# | F# Maj7 | G# min7 | A#m7 ⇒ A#7 ⇒ A#7#5 | B Maj7 | C#7 | D# min7 | E#m7b5 |
- Substitute or Passing Chord to the Mediant chord in F# Major
A#7#5 in B# minor
Although the A#7#5 chord can find a place in the key of B# minor, it might not be as commonly used in this context, and besides that, you won’t find any piece of music written in B# because it’s a theoretical key.
It’s more practical to refer to the C minor key which is the enharmonic equivalent key of B# major.
| Minor Scale | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | C min7 | Dm7b5 | Eb Maj7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 | Bb7 ⇒ Bb7#5 = A#7#5 |
- Substitute or Passing Chord to the Leading Tone chord in C minor as Bb7#5 (less common)
A#7#5 as Substitute for a Secondary Dominant 7th chord
A secondary dominant is a chord that doesn’t belong to the main key of a musical piece but is used to strongly lead to another chord that does. In Western music, the fifth note of the scale has a powerful “dominant” role, creating tension that naturally resolves to the first note of the scale (I). A secondary dominant chord serves the same purpose but directs this dominant function to a different chord, causing a temporary shift away from the main key.
For instance, in the key of G# major, the D#7 chord serves as the V chord, leading back to the I chord of G# Maj7. Introducing an additional chord between G# Maj7 and D#7 that strongly gravitates towards D#7 results in a secondary dominant chord. In this scenario, including an A#7 chord generates a pull towards D#7, as A#7 functions as the V chord in the key of D#.
| G# Maj7 | D#7 |
⇒
| G# Maj7 | A#7 | D#7 |
Instead of using a standard A#7 chord, you can opt for the A#7#5 chord in its place or in combination with it. This substitution or addition can add more tension and complexity to the progression, leading to a more interesting and dynamic musical result.
| G# Maj7 | D#7 |
⇒
| G# Maj7 | A#7/A#7#5 | D#7 |
A#7#5 Chord Function in Major and Minor Keys
A#7#5 as Dominant Chord in D# Major
A#7#5 as Dominant Chord in D# minor
The A#7 chord can also be located on the V degree of the D# harmonic and melodic minor scales. It’s frequently employed in conjunction with chords based on the natural minor scale or as a substitute for the A# min7 chord found in the natural minor scale. In certain contexts, an A#7#5 can be used instead of an A#7 in this role, providing a different harmonic flavor.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| D# min7 | E#m7b5 | F# Maj7 | G# min7 | A# min7 ⇒ A#7 ⇒ A#7#5 | B Maj7 | C#7 |
A#7#5 as V degree on Minor Scale – Chord Progressions
Try playing these chord progressions to get an idea of how A#7#5 functions as the subdominant (V degree) in the key of D# minor. I recommend playing an A#7 chord within the same measure as the A#7#5 chord, as it adds a sense of harmonic movement to the progression.
ii V i
| ii | V | i |
| E#m7b5 | A#7#5 | A#7 | D# min7 |
i iv V
| i | iv | V |
| D# min7 | G# min7 | A#7#5 | A#7 |
i iv VI V
| i | iv | VI | V |
| D# min7 | G# min7 | B Maj7 | A#7#5 | A#7 |
i VI V iv
| i | VI | V | iv |
| D# min7 | B Maj7 | A#7#5 | A#7 | G# min7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| D# min7 | G# min7 | C#7 | F# Maj7 | B Maj7 | E#m7b5 | A#7#5 | A#7 | D# min7 |
A#7#5 as III7 Degree in F# Major
This is a very common substitution of dominant chords in place of minor chords. In the case of A#7, we are in F# major since the minor chord we are going to substitute is on the iii degree of the scale:
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| F# Maj7 | G# min7 | A# min7 ⇒ A#7 ⇒ A#7#5 | B Maj7 | C#7 | D# min7 | E#m7b5 |
A#7#5 as III7 degree – Chord Progressions
Try playing these chord progressions to get an idea of how A#7#5 functions in this position. To understand why this substitution is possible, I suggest checking out some of the posts related to dominant 7th chords. There are different interpretations of this substitution, so it can be helpful to explore them to fully understand its potential use.
I III7 vi
| I | III7 | vi |
| F# Maj7 | A#7#5 | A#7 | D# min7 |
I III7 VI7 ii
| I | III7 | VI7 | ii |
| F# Maj7 | A#7#5 | A#7 | D#7 | G# min7 |
I III7 IV VI7 ii V iii/biiiø ii/V
| I | III7 | IV | VI7 | ii | V | iii/biiiø | ii/V |
| F# Maj7 | A#7#5 | A#7 | B Maj7 | D#7 | G# min7 | C#7 | A# min7 | A dim | G# min7 | C#7 |
A#7#5 as Leading Tone Chord in B# minor
Alternative A#7#5 Nomenclature
- La 7#5
- A# 7+5
- A# aug7
- A# 7(#5)
- A# 7#5th
- A# 7 aug5
- A# Dominant 7th #5
- A# Dominant Seventh Sharp Fifth
Conclusion
The chord progressions and examples presented in this post provide a comprehensive overview of the most common uses of the A#7#5 chord. It’s important to note, however, that there are many advanced harmony-related topics that could not be included due to space constraints. These topics include chord progressions built on harmonic and melodic scales, modal scales, hidden tonality, secondary dominants and other chord substitutions, non-functional harmony and atonal music, modal interchange and borrowed chords, voice leading and counterpoint, chromatisms, jazz harmony…I mean, music theory is a huge topic!
Although I couldn’t cover all of these topics in my post, I encourage readers to continue exploring these areas in their own study and research. By expanding your knowledge in these advanced areas of music theory, you can gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic possibilities that exist beyond the basics presented here.