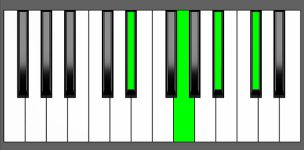
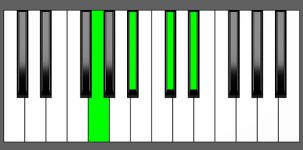
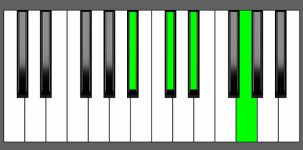
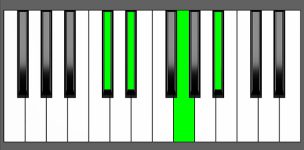
Piano Diagram of D#7 in Root Position

A D#7 chord is a dominant 7th chord built upon the key of D#. It’s made by the root note D#, the major 3rd Fx, the perfect 5th A#, and the minor 7th C#. The D#7 chord can be found on the fifth degree of several scales. Keep reading to understand the music theory behind this chord.
Structure of D#7
Notes |
|---|
| D#, Fx, A#, C# |
Intervals |
|---|
| R, 3, 5, m7 |
Fingers Position
Left Hand |
|---|
| 5, 3, 2, 1
5, 4, 2, 1 |
Right Hand |
|---|
| 1, 2, 3, 5
1, 2, 4, 5 |
D#7 Chord Inversions
The D#7 chord has a total of 3 inversions:
| Root Position: | D# | Fx | A# | C# |
| 1st Inversion: | Fx | A# | C# | D# |
| 2nd Inversion: | A# | C# | D# | Fx |
| 3rd Inversion: | C# | D# | Fx | A# |
Piano Keyboard Diagrams
Music Theory and Harmony of D#7
What are Dominant Seventh Chords?
A dominant 7th chord is a four-note chord that consists of a major triad with a minor 7th added. Dominant 7th chords are important chords in music theory, as they add a sense of tension and instability that can lead to the resolution of the chord. They have a strong pull toward the tonic, making them common in cadences and progressions.
Let’s see how to build this kind of chord:
Building the D#7 Chord: Different Approaches
Starting from the D# Major Scale:
To form a dominant 7th chord, you combine the root, the major 3rd, the 5th, and the minor 7th from a major scale.


To create a D#7 chord, apply the formula R, 3, 5, m7 in the following manner:
- Begin with the Root note D#.
- Select the major 3rd interval, which is Fx, and add it to the chord.
- Add the 5th interval, A#.
- Add the minor 7th interval, which is C#.
By following this simple formula, you can create a dominant 7th chord from any major scale.
by Combining Intervals:
One method to create a dominant 7th chord is by combining specific intervals – a major 3rd, a minor 3rd, and again a minor 3rd.
3 + m3 + m3 = Dominant 7th Chords
For example, to create a D#7 chord, we start with the root note D#.
We then add a major 3rd interval, which is four half-steps up from the root, to get G (Fx).
Next, we add a minor 3rd interval, which is three half-steps up from G, to get A#.
Finally, we add another minor 3rd interval, which is three half-steps up from A#, to get C#. Together, these intervals form the D#7 chord.
Characteristics of the D#7 Chord
Dominant 7th chords are often used as transitional chords to add tension and prepare for the resolution to the tonic. They have a distinct sound that is often described as “bluesy” or “jazzy”. From a theoretical point of view, it is an unstable chord because it contains a tritone, an interval of three whole tones between the 3rd and 7th degree.
The ii-V-I Progression
In the theoretical key of G# major, this progression would involve playing the chords A# minor (ii), D#7 (V), and G# major (I) in sequence.
When played as A# minor, D# major, and G# major, the progression may sound complete but lacks the tension and resolution provided by the D#7 chord. The minor 7th interval adds a layer of tension to the progression, creating a sense of expectation for the resolution to the G# major chord.
How to Use D#7 in a Chord Progression
The D#7 chord is a chord that can be used to add tension, create movement, and establish resolution in your chord progressions. It is commonly employed in all genres, from jazz, rock, and pop to folk and traditional music.
The D#7 chord carries a dominant function, which means it naturally resolves to a chord that represents a point of stability or home within a musical key. Here are some of the most common uses of the D#7 chord:
Most common uses of D#7
These tables show the harmonized major and natural minor scales where you can find a D#7 or use it in place of other chords.
D#7 on Major and minor Scales
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ab = G# | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 = D#7 | F min7 | Gm7b5 |
- Dominant chord in G# Major as Eb7
| Natural Minor | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E# = F | F min7 | Gm7b5 | Ab Maj7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 | Eb7 = D#7 |
- Leading Tone chord in E# minor as Eb7
D#7 as Substitute for D#m7
In this case, the D#7 chord is derived from the harmonic minor scale and is commonly used as a substitute for a D#m7 chord on the V degree.
| Natural Minor | i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G# | G# min7 | A#m7b5 | B Maj7 | C# min7 | D#min7 ⇒ D#7 | E Maj7 | F#7 |
- Dominant chord in G# minor
D#7 in Blues Progressions
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D# = Eb | Eb Maj7 ⇒ Eb7 = D#7 | F min7 | G min7 | Ab Maj7 ⇒ Ab7 | Bb7 | C min7 | Dm7b5 |
| A# = Bb | Bb Maj7 ⇒ Bb7 | C min7 | D min7 | Eb Maj7 ⇒ Eb7 = D#7 | F7 | G min7 | Am7b5 |
| G# = Ab | Ab Maj7 ⇒ Ab7 | Bb min7 | C min7 | Db Maj7 ⇒ Db7 | Eb7 | F min7 | Gm7b5 |
- Tonic chord in Eb Major as Eb7
- Subdominant chord in Bb Major as Eb7
- Dominant chord in Ab Major as Eb7
D#7 in a I III7 Progression
| Major Scale | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | B Maj7 | C# min7 | D#m7 ⇒ D#7 | E Maj7 | F#7 | G# min7 | A#m7b5 |
In a I – III7 chord progression, (B Maj7 | D#7), the III degree, which should be a D# minor chord, is often played as a D#7 chord. There are multiple explanations for this substitution, all of which are correct and provide different interpretations:
1. Dominant Chord Substitution: In the key of B Major, the V degree chord is typically represented by an F#7 chord. However, it is possible to use a diminished 7th chord as a substitute for the dominant 7th just by raising the root of the 7th chord by a half-step. In the case of the F#7 chord, it can be replaced by an G diminished 7th chord (F#, A#, C#, E becomes G, A#, C#, E). By lowering just one note of the G diminished 7th chord, G, A#, C#, E becomes G (Fx), A#, C#, D#, which is an inversion of the D#7 chord.
F#, A#, C#, E ⇒
G, A#, C#, E ⇒
G (Fx), A#, C#, D#
2. Prepared Modulation I – III7 – vi: In B Major, the relative minor key is G# minor. Therefore, introducing the V degree (D#7) of the relative minor key (G#m) as a modulation that resolves on the vi degree (G#m) is a valid explanation for this substitution.
| B Maj7 | G# min7 |
⇒
| B Maj7 | D#7 | G# min7 |
3. Secondary Dominant: In B Major, the V of the VI degree (G#m) is D#.
D#7 in a Tritone Substitution
The term “Tritone Substitution” is a musical concept where a dominant 7th chord is replaced by another dominant 7th chord that is a tritone away. This means that instead of using the original dominant chord, a musician substitutes it with a chord that is located six semitones above or below the original.
In the context of a ii-V-I chord progression, which is a common jazz chord progression, the tritone substitution can be represented as “ii-SubV7-I”. This means that the ii chord is followed by a substitute dominant 7th chord, which then resolves to the I chord.
| ii | V | I |
| E min7 | A7 | D Maj7 |
| ii | SubV7 | I |
| E min7 | Eb7 = D#7 | D Maj7 |
This type of substitution works because shares the third and 7th notes. This creates a chromatic movement that adds interest and tension, leading toward the tonic chord. The tritone substitution works because the substitute dominant chord shares the same 3rd and 7th notes as the original dominant chord but in reverse order.
For example, if the original dominant chord is A7 (A, C#, E, G), the substitute dominant chord would be D#7 (D#, Fx, A#, C#), as both chords share the notes C# and G (Fx), which are the 3rd and 7th notes.
It’s important to note that D#7 is a non-diatonic chord in the key of D. This means that while it may sound good in certain musical contexts, it’s important to be careful and not clash with the melody or other harmonic elements of the composition.
D#7 as Secondary Dominant chord
A secondary dominant is a type of chord that is not in the main key of a musical piece but is used to create a strong pull toward another chord that is. In Western music, the fifth scale degree has a strong “dominant” function and creates tension that resolves to the first scale degree chord (I). A secondary dominant chord is used to create this same dominant function but toward a different chord, leading to a temporary departure from the main key.
| C# Maj7 | G#7 | ⇒
| C# Maj7 | D#7 | G#7 |
Let’s take the key of C# major as an example. In this key, the G#7 chord acts as the dominant V chord, leading back to the C# Maj7 chord, which is our tonic I chord. Now, if we want to add an extra chord between C# Maj7 and G#7 that creates a strong pull toward G#7, we introduce a secondary dominant chord. To achieve this, we can use a D#7 chord because in the key of G#, D#7 serves as the dominant V chord. This way, the D#7 chord enhances the tension and directs our ears toward the resolution on G#7.
D#7 as Dominant Chord in G# Major
D#7 as the Leading Tone Chord in E# minor
D#7 as Dominant chord in G# minor
D#7 can be found also on the G# harmonic minor scale, as it is the V chord in that scale. It’s very common to use this chord in combination with chords built on the natural minor scale or to substitute it for the D# min7 chord that is present in the natural minor scale.
| i | ii | III | iv | v | VI | VII |
| G# min7 | A#m7b5 | B Maj7 | C# min7 | D# min7 ⇒ D#7 | E Maj7 | F#7 |
D#7 as V degree on Minor Scale – Chord Progressions
Try playing these chord progressions to get an idea of how D#7 functions as the subdominant (V degree) in the G# minor key.
ii V7 i
| ii | V7 | i |
| A#m7b5 | D#7 | G# min7 |
i iv V7
| i | iv | V7 |
| G# min7 | C# min7 | D#7 |
i iv VI V7
| i | iv | VI | V7 |
| G# min7 | C# min7 | E Maj7 | D#7 |
i V7 VI VII
| i | V7 | VI | VII |
| G# min7 | D#7 | E Maj7 | F#7 |
i VI V7 iv
| i | VI | V7 | iv |
| G# min7 | E Maj7 | D#7 | C# min7 |
Circle Progression
| i | iv | VII | III | VI | ii | V7 | i |
| G# min7 | C# min7 | F#7 | B Maj7 | E Maj7 | A#m7b5 | D#7 | G# min7 |
D#7 as Tonic Chord in a Blues Progression in D#
In the theoretical key of D# major, the first chord is a D# Maj7 but in some contexts, it can be substituted with a D#7.
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| D# Maj7 ⇒ D#7 | E# min7 | Fx min7 | G# Maj7 ⇒ G#7 | A#7 | B# min7 | Cxm7b5 |
One such context is in the blues genre, where the use of dominant 7th chords as tonics is common.
Blues music draws its foundation from the Mixolydian scale, which is a variation of the major scale. The Mixolydian scale is characterized by having a flattened 7th note compared to the major scale.
When we consider the key of D# major, the 7th note is Cx (D). However, in the Mixolydian scale used in blues music, the 7th note is flattened, which means it is lowered by a half step. Consequently, the Cx note in the D# major scale becomes a C# in the Mixolydian scale.
This alteration of the 7th note from Cx to C# natural in the Mixolydian scale is significant because it creates a minor 7th interval. In other words, when we build a dominant 7th chord on the tonic D# using the Mixolydian scale, we get a D#7 chord.
It is this altered 7th note and the resulting minor 7th interval that contributes to the bluesy and soulful atmosphere associated with the genre.
In the context of blues music, a D#7 chord can serve as:
- the tonic chord (I) in the key of D#,
- the subdominant (IV) in the key of A#,
- the dominant chord (V) in the key of G#.
However, since D# Major is a theoretical key, I suggest referring to its enharmonic equivalent key Eb Major.
This is because blues music uses a specific chord progression known as the 12-bar blues, which consists of three chords played over 12 bars.
| I | I | I | I |
| IV | IV | I | I |
| V | IV | I | V |
D#7 as I degree in a Blues Progression in D#
In the key of D#, the 12-bar blues progression would typically be D#7 (I), G#7 (IV), and A#7 (V) chords, with the D#7 chord serving as the tonic and the other two chords as the subdominant and dominant, respectively.
Blues Chord Progression in D#
| I7 | IV7 | I7 | V | IV7 | I7 | V | |||||
| D#7 | D#7 | D#7 | D#7 | G#7 | G#7 | D#7 | D#7 | A#7 | G#7 | D#7 | A#7 |
Blues Chord Progression in D# – Variation
| I7 | IV7 | I7 | IV7 | I7 | V | IV7 | I7 | IV7 | I7 | V | |||
| D#7 | G#7 | D#7 | D#7 | G#7 | G#7 | D#7 | D#7 | A#7 | G#7 | D#7 | G#7 | D#7 | A#7 |
D#7 as Subdominant Chord in a Blues Progression in A#
Check Eb7 in a Blues Progression in Bb
D#7 as Dominant Chord in a Blues Progression in G#
Check Eb7 in a Blues Progression in Ab
D#7 as III7 Degree in B Major
This is a very common substitution of dominant chords in place of minor chords. In the case of D#7, we are in B major since the minor chord we are going to substitute is on the iii degree of the scale:
| I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii |
| B Maj7 | C# min7 | D# min7 | E Maj7 | F#7 | G# min7 | A#m7b5 |
D#7 as III7 degree – Chord Progressions
Try playing these chord progressions to get an idea of how D#7 functions on the 3rd degree in the B Major key.
I III7 vi
| I | III7 | vi |
| B Maj7 | D#7 | G# min7 |
I III7 VI7 ii
| I | III7 | VI7 | ii |
| B Maj7 | D#7 | G#7 | C# min7 |
I III7 IV VI7 ii V iii/biiiø ii/V
| I | III7 | IV | VI7 | ii | V | iii/biiiø | ii/V |
| B Maj7 | D#7 | E Maj7 | G#7 | C# min7 | F#7 | D# min7 | D dim | C# min7 | F#7 |
Alternative D#7 Nomenclature
- D#7
- Re#7
- D# 7th
- D# dom7
- D# dominant 7th
Conclusion
The chord progressions and examples presented in this post provide a comprehensive overview of the most common uses of the D#7 chord. It’s important to note, however, that many advanced harmony-related topics could not be included due to space constraints. These topics include chord progressions built on harmonic and melodic scales, modal scales, hidden tonality, secondary dominants and other chord substitutions, non-functional harmony and atonal music, modal interchange and borrowed chords, voice leading and counterpoint, chromatisms, jazz harmony…I mean, music theory is a huge topic!
Although I couldn’t cover all of these topics in my post, I encourage readers to continue exploring these areas in their own study and research. By expanding your knowledge in these advanced areas of music theory, you can gain a deeper understanding of the harmonic possibilities that exist beyond the basics presented here.